Lymphatic system anomalies in Crouzon syndrome
- PMID: 21686735
- PMCID: PMC3030293
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr.07.2008.0586
Lymphatic system anomalies in Crouzon syndrome
Abstract
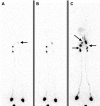
Crouzon syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterised mainly by distinctive malformations of the skull and facial region and caused by mutations in the fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) gene. No study reported on oedemas related to lymphatic system abnormalities in these patients. A case of Crouzon syndrome displaying classic facial anomalies but also with bilateral lower limb oedema is reported in whom lymphoscintigraphic investigation of the limbs clearly delineated the presence of lymphatic system anomalies.
Figures
References
-
- Fries PD, Katowitz JA. Congenital craniofacial anomalies of ophthalmic importance. Surv Ophthalmol 1990; 35: 87–119 - PubMed
-
- Oldridge M, Wilkie AO, Slaney SF, et al. Mutations in the third immunoglobulin domain of the fibroblast growth factor receptor-2 gene in Crouzon syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 1995; 4: 1077–82 - PubMed
-
- Bourgeois P, Munck D, Sales F. Anomalies of thoracic lymph duct drainage demonstrated by lymphoscintigraphy and review of the literature about these anomalies. Eur J Surg Oncol 2008; 34: 553–5 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous