Lymphoedema: a paradoxical effect of tumour necrosis factor inhibitors - case report and review of literature
- PMID: 21686765
- PMCID: PMC3027781
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr.07.2008.0520
Lymphoedema: a paradoxical effect of tumour necrosis factor inhibitors - case report and review of literature
Abstract
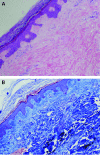
This report describes the development of lymphoedema in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who was treated with tumour necrosis factor α (TNFα) inhibitors.The patient was a 62-year-old woman with a long-standing history of RA that had been uncontrolled with steroids and methotrexate. Eight months after initiation of treatment with TNFα inhibitors she developed progressive symmetrical ascending non-pitting oedema of both legs with extensive keratinisation. A diagnosis of lymphoedema was made based on the clinical presentation and exclusion of alternative diagnoses. Skin biopsy showed dermatosclerosis consistent with lymphoedema. The temporal relationship suggested a link between the initiation of TNFα inhibitors and the development of lymphoedema. TNFα inhibitors are widely used to treat inflammatory diseases including lymphoedema. Paradoxically, there are reports suggesting the appearance of psoriasis, vasculitis and other inflammatory cutaneous conditions after the use of TNFα inhibitors. A review of literature is also presented.
Figures
References
-
- Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1988; 31: 315–24 - PubMed
-
- Cho S, Atwood JE. Peripheral edema. Am J Med 2002; 113: 580–6 - PubMed
-
- Guillevin L, Mouthan L. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha blockade and the risk of vasculitis. J Rheumatol 2004; 31: 1885–6 - PubMed
-
- Mang R, Ruzicka T, Stege H. Therapy for severe necrotizing vasculitis with infliximab. J Am Acad Dermatol 2004; 51: 321–2 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources