Enteropathy associated T cell lymphoma: common in coeliac disease
- PMID: 21686880
- PMCID: PMC3029034
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr.06.2008.0270
Enteropathy associated T cell lymphoma: common in coeliac disease
Abstract
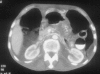
A 56-year-old male admitted with haematemesis and epigastric pain and severe weight loss on a background of coeliac disease. Computed tomography (CT) abdomen revealed a thickening of the mucosal folds of a short segment of jejunum. He deteriorated and had an exploratory laparotomy and bowel resection with side-side jejojejunal stapled anastomosis and extended right hemicolectomy and ileocolic anastomosis. Histology demonstrated multifocal high-grade malignant T cell lymphoma. Coeliac disease is a very common lifelong disorder. It is associated with osteoporosis, infertility, autoimmune disorders and increased risk of malignancy including an increased risk of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) especially of the T cell type. Enteropathy-type T cell lymphoma is associated with a very poor prognosis. There is significant evidence that adherence to a gluten-free diet decreases the risk of developing enteropathy-type T cell lymphoma and helps to prevent development of autoimmune diseases, diabetes mellitus and osteoporosis in patients with coeliac disease.
Figures




References
-
- Dewar DH, Ciclitira PJ. Clinical features and diagnosis of celiac disease. Gastroenterology 2005; 128(1 Suppl): 19–24S - PubMed
-
- Catassi C, Ratsch IM, Fabiani E, et al. Coeliac disease in the year 2000: exploring the iceberg. Lancet 1994; 343: 200–3 - PubMed
-
- Green PH, Cellier C. Celiac disease. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 1731–43 - PubMed
-
- Mäki M, Mustalahti K, Kokkonen J, et al. Prevalence of celiac disease among children in Finland. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 2517–24 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
