Biomarkers in overactive bladder: a new objective and noninvasive tool?
- PMID: 21687625
- PMCID: PMC3113283
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/382431
Biomarkers in overactive bladder: a new objective and noninvasive tool?
Abstract
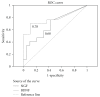
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) is a highly prevalent urinary dysfunction, with considerable economic and human costs. Clinical diagnosis of OAB is still based on subjective symptoms. A new accurate, objective and noninvasive test to diagnose OAB and assess therapeutic outcome is lacking. Recent studies in lower urinary tract (LUT) dysfunctions, particularly in OAB patients, indicate that urinary proteins (neurotrophins, prostaglandins, and cytokines), serum C reactive protein, and detrusor wall thickness are altered, and such changes could be used as biomarkers of the disease. Nowadays, increasing emphasis has been given to the role of urinary neurotrophins, namely nerve growth factor (NGF) and brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), as key players in some urinary dysfunctions. Although recently considered to be a bladder dysfunction biomarker, urinary NGF presents low sensitivity and specificity. Preliminary results suggest that BDNF may serve as a more efficient biomarker. Even though we have to wait for future studies to confirm the potential role of NGF and BDNF as OAB biomarkers, it is already clear that neurotrophins will contribute to elucidate the physiopathological basis of OAB. Herein are reviewed the latest advances in this new and exciting field, the detection and clinical application of emerging OAB biomarkers.
Figures
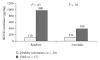
References
-
- Irwin DE, Milsom I, Hunskaar S, et al. Population-based survey of urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, and other lower urinary tract symptoms in five countries: results of the EPIC study. European Urology. 2006;50(6):1306–1315. - PubMed
-
- Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the standardisation sub-committee of the international continence society. Neurourology and Urodynamics. 2002;21(2):167–178. - PubMed
-
- Chapple CR, Artibani W, Cardozo LD, et al. The role of urinary urgency and its measurement in the overactive bladder symptom syndrome: current concepts and future prospects. British Journal of Urology International. 2005;95(3):335–340. - PubMed
-
- Nixon A, Colman S, Sabounjian L, et al. A validated patient reported measure of urinary urgency severity in overactive bladder for use in clinical trials. Journal of Urology. 2005;174(2):604–607. - PubMed
-
- Starkman JS, Dmochowski RR. Urgency assessment in the evaluation of overactive bladder (OAB) Neurourology and Urodynamics. 2008;27(1):13–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

