Continuous non-invasive monitoring of tidal volumes by measurement of tidal impedance in neonatal piglets
- PMID: 21687746
- PMCID: PMC3110249
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021003
Continuous non-invasive monitoring of tidal volumes by measurement of tidal impedance in neonatal piglets
Abstract
Background: Electrical Impedance measurements can be used to estimate the content of intra-thoracic air and thereby give information on pulmonary ventilation. Conventional Impedance measurements mainly indicate relative changes, but no information concerning air-volume is given. The study was performed to test whether a 3-point-calibration with known tidal volumes (VT) during conventional mechanical ventilation (CMV) allows subsequent calculation of VT from total Tidal-Impedance (tTI) measurements using Quadrant Impedance Measurement (QIM). In addition the distribution of TI in different regions of the thorax was examined.
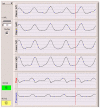
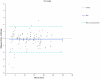
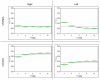
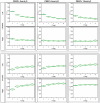
Methodology and principal findings: QIM was performed in five neonatal piglets during volume-controlled CMV. tTI values at three different VT (4, 6, 8 ml/kg) were used to establish individual calibration curves. Subsequently, each animal was ventilated with different patterns of varying VT (2-10 ml/kg) at different PEEP levels (0, 3, 6, 9, 12 cmH(2)O). VT variation was repeated after surfactant depletion by bronchoalveolar lavage. VT was calculated from tTI values (VT(calc)) and compared to the VT delivered by the ventilator (VT(PNT)). Bland-Altman analysis revealed good agreement between VT(calc) and VT(PNT) before (bias -0.08 ml; limits of agreement -1.18 to 1.02 ml at PEEP = 3 cmH(2)O) and after surfactant depletion (bias -0.17 ml; limits of agreement -1.57 to 1.22 ml at PEEP = 3 cmH(2)O). At higher PEEP levels VT(calc) was lower than VT(PNT), when only one fixed calibration curve (at PEEP 3 cmH(2)O) was used. With a new calibration curve at each PEEP level the method showed similar accuracy at each PEEP level. TI showed a homogeneous distribution over the four assessed quadrants with a shift toward caudal regions of the thorax with increasing VT.
Conclusion: Tidal Impedance values could be used for precise and accurate calculation of VT during CMV in this animal study, when calibrated at each PEEP level.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Dellaca' RL, Ventura ML, Zannin E, Natile M, Pedotti A, et al. Measurement of total and compartmental lung volume changes in newborns by optoelectronic plethysmography. Pediatr.Res. 2010;67:11–16. - PubMed
-
- Wolf GK, Arnold JH. Noninvasive assessment of lung volume: respiratory inductance plethysmography and electrical impedance tomography. Crit Care Med. 2005;33:S163–9. - PubMed
-
- Harris ND, Suggett AJ, Barber DC, Brown BH. Applications of applied potential tomography (APT) in respiratory medicine. Clin Phys Physiol Meas. 1987;8(Suppl A):155–165. - PubMed
-
- Adams JA, Zabaleta IA, Stroh D, Sackner MA. Measurement of breath amplitudes: comparison of three noninvasive respiratory monitors to integrated pneumotachograph. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1993;16:254–258. - PubMed
-
- Frerichs I. Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) in applications related to lung and ventilation: a review of experimental and clinical activities. Physiol Meas. 2000;21:R1–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

