Traditional chinese medicine improves activities of daily living in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 21687764
- PMCID: PMC3109418
- DOI: 10.4061/2011/789506
Traditional chinese medicine improves activities of daily living in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
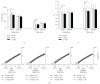
We evaluated the effects of a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), named Zeng-xiao An-shen Zhi-chan 2 (ZAZ2), on patients with Parkinson's disease (PD). Among 115 patients with idiopathic PD enrolled (mean age, 64.7 ± 10.2 years old), 110 patients (M = 65, F = 45; mean age, 64.9 ± 10.7 years old) completed the study. Patients took either ZAZ2 (n = 59) or placebo granule (n = 56) in a blind manner for 13 weeks while maintaining other anti-Parkinson medications unchanged. All participants wore a motion logger, and we analyzed the power-law temporal autocorrelation of the motion logger records taken on 3 occasions (before, one week, and 13 weeks after the drug administration). Drug efficacy was evaluated with the conventional Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS), as well as the power-law exponent α, which corresponds to the level of physical activity of the patients. ZAZ2 but not placebo granule improved the awake-sleep rhythm, the UPDRS Part II, Part II + III, and Part IV scores, and the α values. The results indicate that ZAZ2 improved activities of daily living (ADL) of parkinsonism and, thus, is a potentially suitable drug for long-term use.
Figures

References
-
- Pahwa R, Factor SA, Lyons KE, et al. Practice parameter: treatment of parkinson disease with motor fluctuations and dyskinesia (an evidence-based review): report of the quality standards subcommittee of the american academy of neurology. Neurology. 2006;66(7):983–995. - PubMed
-
- Hobson DE, Lang AE, Martin WR, Razmy A, Rivest J, Fleming J. Excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden-onset sleep in Parkinson disease: a survey by the Canadian movement disorders group. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2002;287(4):455–463. - PubMed
-
- Comella CL. Daytime sleepiness, agonist therapy, and driving in Parkinson disease. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2002;287(4):509–511. - PubMed
-
- Arnulf I, Konofal E, Merino-Andreu M, et al. Parkinson’s disease and sleepiness: an integral part of PD. Neurology. 2002;58(7):1019–1024. - PubMed
-
- Ondo WG, Dat Vuong K, Khan H, Atassi F, Kwak C, Jankovic J. Daytime sleepiness and other sleep disorders in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology. 2001;57(8):1392–1396. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

