Effects of diet type and supplementation of glucosamine, chondroitin, and MSM on body composition, functional status, and markers of health in women with knee osteoarthritis initiating a resistance-based exercise and weight loss program
- PMID: 21689421
- PMCID: PMC3141631
- DOI: 10.1186/1550-2783-8-8
Effects of diet type and supplementation of glucosamine, chondroitin, and MSM on body composition, functional status, and markers of health in women with knee osteoarthritis initiating a resistance-based exercise and weight loss program
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to determine whether sedentary obese women with knee OA initiating an exercise and weight loss program may experience more beneficial changes in body composition, functional capacity, and/or markers of health following a higher protein diet compared to a higher carbohydrate diet with or without GCM supplementation.
Methods: Thirty sedentary women (54 ± 9 yrs, 163 ± 6 cm, 88.6 ± 13 kg, 46.1 ± 3% fat, 33.3 ± 5 kg/m2) with clinically diagnosed knee OA participated in a 14-week exercise and weight loss program. Participants followed an isoenergenic low fat higher carbohydrate (HC) or higher protein (HP) diet while participating in a supervised 30-minute circuit resistance-training program three times per week for 14-weeks. In a randomized and double blind manner, participants ingested supplements containing 1,500 mg/d of glucosamine (as d-glucosamine HCL), 1,200 mg/d of chondroitin sulfate (from chondroitin sulfate sodium), and 900 mg/d of methylsulfonylmethane or a placebo. At 0, 10, and 14-weeks, participants completed a battery of assessments. Data were analyzed by MANOVA with repeated measures.
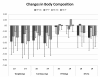
Results: Participants in both groups experienced significant reductions in body mass (-2.4 ± 3%), fat mass (-6.0 ± 6%), and body fat (-3.5 ± 4%) with no significant changes in fat free mass or resting energy expenditure. Perception of knee pain (-49 ± 39%) and knee stiffness (-42 ± 37%) was decreased while maximal strength (12%), muscular endurance (20%), balance indices (7% to 20%), lipid levels (-8% to -12%), homeostasis model assessment for estimating insulin resistance (-17%), leptin (-30%), and measures of physical functioning (59%), vitality (120%), and social function (66%) were improved in both groups with no differences among groups. Functional aerobic capacity was increased to a greater degree for those in the HP and GCM groups while there were some trends suggesting that supplementation affected perceptions of knee pain (p < 0.08).
Conclusions: Circuit style resistance-training and weight loss improved functional capacity in women with knee OA. The type of diet and dietary supplementation of GCM provided marginal additive benefits.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT01271218.
Figures
References
-
- Dillon CF, Rasch EK, Gu Q, Hirsch R. Prevalence of knee osteoarthritis in the United States: arthritis data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1991-94. J Rheumatol. 2006;33:2271–2279. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous