Diffusion model for one-choice reaction-time tasks and the cognitive effects of sleep deprivation
- PMID: 21690336
- PMCID: PMC3131321
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1100483108
Diffusion model for one-choice reaction-time tasks and the cognitive effects of sleep deprivation
Abstract
One-choice reaction-time (RT) tasks are used in many domains, including assessments of motor vehicle driving and assessments of the cognitive/behavioral consequences of sleep deprivation. In such tasks, subjects are asked to respond when they detect the onset of a stimulus; the dependent variable is RT. We present a cognitive model for one-choice RT tasks that uses a one-boundary diffusion process to represent the accumulation of stimulus information. When the accumulated evidence reaches a decision criterion, a response is initiated. This model is distinct in accounting for the RT distributions observed for one-choice RT tasks, which can have long tails that have not been accurately captured by earlier cognitive modeling approaches. We show that the model explains performance on a brightness-detection task (a "simple RT task") and on a psychomotor vigilance test. The latter is used extensively to examine the clinical and behavioral effects of sleep deprivation. For the brightness-detection task, the model explains the behavior of RT distributions as a function of brightness. For the psychomotor vigilance test, it accounts for lapses in performance under conditions of sleep deprivation and for changes in the shapes of RT distributions over the course of sleep deprivation. The model also successfully maps the rate of accumulation of stimulus information onto independently derived predictions of alertness. The model is a unified, mechanistic account of one-choice RT under conditions of sleep deprivation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
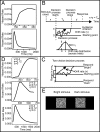
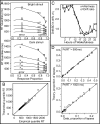

References
-
- Cooper JM, Strayer DL. Effects of simulator practice and real-world experience on cell-phone–related driver distraction. Hum Factors. 2008;50:893–902. - PubMed
-
- Gunzelmann G, Byrne MD, Gluck KA, Moore LR., Jr Using computational cognitive modeling to predict dual-task performance with sleep deprivation. Hum Factors. 2009;51:251–260. - PubMed
-
- Wagenmakers EJ. Methodological and empirical developments for the Ratcliff diffusion model of response times and accuracy. Eur J Cogn Psychol. 2009;21:641–671.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

