Transcriptional regulation of MG_149, an osmoinducible lipoprotein gene from Mycoplasma genitalium
- PMID: 21692875
- PMCID: PMC3196619
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07717.x
Transcriptional regulation of MG_149, an osmoinducible lipoprotein gene from Mycoplasma genitalium
Abstract
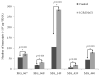
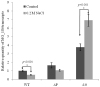
Transcriptional regulation remains poorly understood in Mycoplasma genitalium, the smallest self-replicating cell and the causative agent of a spectrum of urogenital diseases. Previously, we reported that MG_149, a lipoprotein-encoding gene, was highly induced under physiological hyperosmolarity conditions. In this study we further analysed MG_149 transcription with a focus on the identification of promoter elements and regulatory mechanisms. We established MG_149 as a genuine osmoinducible gene that exhibited the highest transcript abundance compared with other lipoprotein genes. Using genetic approaches, we demonstrated that the -10 region of the MG_149 promoter was essential for osmoinduction. Moreover, we showed that MG_149 osmoinduction was regulated by DNA supercoiling, as the presence of novobiocin decreased MG_149 expression in a dose-dependent manner. Taken together, these results indicate that DNA supercoiling participates in controlling MG_149 expression during in vivo-like conditions.
© 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
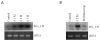

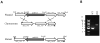



Comment in
-
Regulation of transcription by DNA supercoiling in Mycoplasma genitalium: global control in the smallest known self-replicating genome.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Jul;81(2):302-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07718.x. Epub 2011 Jun 16. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21631605
References
-
- Alice AF, Sanchez-Rivas C. DNA supercoiling and osmoresistance in Bacillus subtilis 168. Curr Microbiol. 1997;35:309–315. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

