Peripheral and central GLP-1 receptor populations mediate the anorectic effects of peripherally administered GLP-1 receptor agonists, liraglutide and exendin-4
- PMID: 21693680
- PMCID: PMC3138234
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2011-0174
Peripheral and central GLP-1 receptor populations mediate the anorectic effects of peripherally administered GLP-1 receptor agonists, liraglutide and exendin-4
Abstract
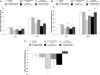
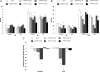
The long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists, exendin-4 and liraglutide, suppress food intake and body weight. The mediating site(s) of action for the anorectic effects produced by peripheral administration of these GLP-1R agonists are not known. Experiments addressed whether food intake suppression after i.p. delivery of exendin-4 and liraglutide is mediated exclusively by peripheral GLP-1R or also involves direct central nervous system (CNS) GLP-1R activation. Results showed that CNS delivery [third intracerebroventricular (3(rd) ICV)] of the GLP-1R antagonist exendin-(9-39) (100 μg), attenuated the intake suppression by i.p. liraglutide (10 μg) and exendin-4 (3 μg), particularly at 6 h and 24 h. Control experiments show that these findings appear to be based neither on the GLP-1R antagonist acting as a nonspecific competing orexigenic signal nor on blockade of peripheral GLP-1R via efflux of exendin-(9-39) to the periphery. To assess the contribution of GLP-1R expressed on subdiaphragmatic vagal afferents to the anorectic effects of liraglutide and exendin-4, food intake was compared in rats with complete subdiaphragmatic vagal deafferentation and surgical controls after i.p. delivery of the agonists. Both liraglutide and exendin-4 suppressed food intake at 3 h, 6 h, and 24 h for controls; for subdiaphragmatic vagal deafferentation rats higher doses of the GLP-1R agonists were needed for significant food intake suppression, which was observed at 6 h and 24 h after liraglutide and at 24 h after exendin-4.
Conclusion: Food intake suppression after peripheral administration of exendin-4 and liraglutide is mediated by activation of GLP-1R expressed on vagal afferents as well as direct CNS GLP-1R activation.
Figures

References
-
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention 2009. Overweight and obesity: data and statistics. Center for Disease Control and Prevention. www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/trends.html
-
- Ogden CL, Yanovski SZ, Carroll MD, Flegal KM. 2007. The epidemiology of obesity. Gastroenterology 132:2087–2102 - PubMed
-
- Merchenthaler I, Lane M, Shughrue P. 1999. Distribution of pre-pro-glucagon and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor messenger RNAs in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 403:261–280 - PubMed
-
- Mojsov S, Kopczynski MG, Habener JF. 1990. Both amidated and nonamidated forms of glucagon-like peptide I are synthesized in the rat intestine and the pancreas. J Biol Chem 265:8001–8008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

