Efficacy and tolerability of Laxatan Granulat in patients with chronic constipation
- PMID: 21694832
- PMCID: PMC3108648
- DOI: 10.2147/ceg.s6236
Efficacy and tolerability of Laxatan Granulat in patients with chronic constipation
Abstract
Background: On average 12% of the population worldwide suffer from acute or chronic constipation. Pathological intestine alterations, an unhealthy diet with reduced liquid intake, and little exercise are potential reasons. Often the motility of the intestine is disturbed. Changing nutrition habits or lifestyle is not always successful. In such cases, laxatives containing macrogol and inulin are highly effective.
Methodology: The efficacy and tolerability of Laxatan(®) Granulat, a laxative containing macrogol, inulin, and mineral salts, was assessed in a drug-monitoring study of 105 patients for four weeks.
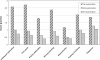
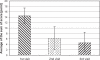
Results: At the end of this study, a highly significant reduction of the constipation symptoms in 98.1% of the patients was observed. No adverse events were reported during this drug-monitoring study. The overall efficacy was rated as being "very good" or "good" for 96% and the overall tolerability was rated as being "very good" or "good" for 99% of patients.
Conclusion: The combination of macrogol, inulin, and mineral salts is highly effective in the treatment of chronic constipation. Due to its prebiotic activity, inulin probably leads to proliferation of lactic acid-producing bacteria. The lowered pH and increased water content probably increases the peristaltic action and therefore reduces constipation.
Keywords: Laxatan®; constipation; inulin; macrogol.
Figures
References
-
- Foxx-Orenstein AE, McNally MA, Odunsi ST. Update on constipation: one treatment does not fit all. Cleve Clin J Med. 2008;75:813–824. - PubMed
-
- Muller-Lissner SA, Kamm MA, Scarpignato C, Wald A. Myths and misconceptions about chronic constipation. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100:232–242. - PubMed
-
- DiPiro JT, Michael KA, Clark BA, et al. Absorption of polyethylene glycol after administration of a PEG-electrolyte lavage solution. Clin Pharm. 1986;5:153–155. - PubMed
-
- Schiller LR, Emmett M, Santa Ana CA, Fordtran JS. Osmotic effects of polyethylene glycol. Gastroenterology. 1988;94:933–941. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources