The roles of ABCA12 in keratinocyte differentiation and lipid barrier formation in the epidermis
- PMID: 21695020
- PMCID: PMC3117010
- DOI: 10.4161/derm.3.2.15136
The roles of ABCA12 in keratinocyte differentiation and lipid barrier formation in the epidermis
Abstract
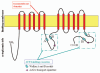
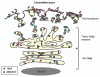
ABCA12 is a member of the large superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters, which bind and hydrolyze ATP to transport various molecules across limiting membranes or into vesicles. The ABCA subfamily members are thought to be lipid transporters. ABCA12 is a keratinocyte transmembrane lipid transporter protein associated with the transport of lipids in lamellar granules to the apical surface of granular layer keratinocytes. Extracellular lipids, including ceramide, are thought to be essential for skin barrier function. ABCA12 mutations are known to underlie the three main types of autosomal recessive congenital ichthyoses: harlequin ichthyosis, lamellar ichthyosis and congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma. ABCA12 mutations lead to defective lipid transport via lamellar granules in the keratinocytes, resulting in malformation of the epidermal lipid barrier and ichthyosis phenotypes. Studies of ABCA12-deficient model mice indicate that lipid transport by ABCA12 is also indispensable for intact differentiation of keratinocytes.
Keywords: ABCA12; congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma; harlequin ichthyosis; lamellar granules; lamellar ichthyosis.
Figures


References
-
- Annilo T, Shulenin S, Chen ZQ, Arnould I, Prades C, Lemoine C, et al. Identification and characterization of a novel ABCA subfamily member, ABCA12, located in the lamellar ichthyosis region on 2q34. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2002;98:169–176. - PubMed
-
- Borst P, Elferink RO. Mammalian ABC transporters in health and disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002;71:537–592. - PubMed
-
- Peelman F, Labeur C, Vanloo B, Roosbeek S, Devaud C, Duverger N, et al. Characterization of the ABCA transporter subfamily: identification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic members, phylogeny and topology. J Mol Biol. 2003;325:259–274. - PubMed
-
- Sakai K, Akiyama M, Sugiyama-Nakagiri Y, McMillan JR, Sawamura D, Shimizu H. Localization of ABCA12 from Golgi apparatus to lamellar granules in human upper epidermal keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol. 2007;16:920–926. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
