The public health impact of coccidioidomycosis in Arizona and California
- PMID: 21695034
- PMCID: PMC3118883
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph8041150
The public health impact of coccidioidomycosis in Arizona and California
Abstract
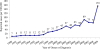
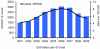
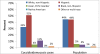
The numbers of reported cases of coccidioidomycosis in Arizona and California have risen dramatically over the past decade, with a 97.8% and 91.1% increase in incidence rates from 2001 to 2006 in the two states, respectively. Of those cases with reported race/ethnicity information, Black/African Americans in Arizona and Hispanics and African/Americans in California experienced a disproportionately higher frequency of disease compared to other racial/ethnic groups. Lack of early diagnosis continues to be a problem, particularly in suspect community-acquired pneumonia, underscoring the need for more rapid and sensitive tests. Similarly, the inability of currently available therapeutics to reduce the duration and morbidity of this disease underscores the need for improved therapeutics and a preventive vaccine.
Keywords: azoles; coccidioidomycosis; community-acquired pneumonia; diagnostics; vaccine.
Figures






References
-
- Fisher F, Bultman MW, Pappagianis D. Operational Guidelines for Geological Fieldwork in Areas Endemic for Coccidioidomycosis (Valley Fever) U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report; U.S. Department of the Interior; Washington, DC, USA: 2000. pp. 1–16.
-
- Stevens DA. Coccidioidomycosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995;332:1077–1082. - PubMed
-
- Chiller TM, Galgiani JN, Stevens DA. Coccidioidomycosis. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2003;17:41–57. - PubMed
-
- Blair JE. Coccidioidomycosis in patients who have undergone transplantation. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2007;1111:365–376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

