Investigating mechanisms of chronic kidney disease in mouse models
- PMID: 21695449
- PMCID: PMC3199379
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-011-1938-2
Investigating mechanisms of chronic kidney disease in mouse models
Abstract
Animal models of chronic kidney disease (CKD) are important experimental tools that are used to investigate novel mechanistic pathways and to validate potential new therapeutic interventions prior to pre-clinical testing in humans. Over the past several years, mouse CKD models have been extensively used for these purposes. Despite significant limitations, the model of unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) has essentially become the high-throughput in vivo model, as it recapitulates the fundamental pathogenetic mechanisms that typify all forms of CKD in a relatively short time span. In addition, several alternative mouse models are available that can be used to validate new mechanistic paradigms and/or novel therapies. Here, we review several models-both genetic and experimentally induced-that provide investigators with an opportunity to include renal functional study end-points together with quantitative measures of fibrosis severity, something that is not possible with the UUO model.
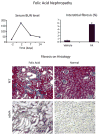
Figures
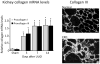


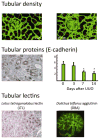

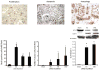

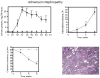

References
-
- Risdon RA, Sloper JC, de Vardener HE. Relationship between renal function and histologic changes found in renal-biopsy specimens from patients with persistent glomerulonephritis. Lancet. 1968;2:363–366. - PubMed
-
- Oda T, Jung YO, Kim H, Cai x, Lopez-Guisa J, Ikeda Y, Eddy AA. PAI-1 deficiency attenuates the fibrogenic response to ureteral obstruction. Kidney Int. 2001;60:587–596. - PubMed
-
- Jones CL, Buch S, Post M, McCulloch L, Liu E, Eddy AA. The pathogenesis of interstitial fibrosis in chronic purine aminonucleoside nephrosis. Kidney Int. 1991;40:1020–1031. - PubMed
-
- Fogo AB, Alpers CE. Navigating the challenges of fibrosis assessment: land in sight? J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22:11–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R03 DK083648/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03DK083648/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054500/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK080926/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08DK080926/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK073497/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50DK44757/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK058925/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03DK58925/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DK044757/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK54500/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08DK073497/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

