Wet nanoscale imaging and testing of polymersomes
- PMID: 21695783
- PMCID: PMC3325755
- DOI: 10.1002/smll.201100511
Wet nanoscale imaging and testing of polymersomes
Figures
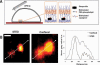

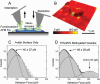
Similar articles
-
Polyethylene glycol as a novel resist and sacrificial material for generating positive and negative nanostructures.Small. 2008 Jul;4(7):920-4. doi: 10.1002/smll.200701089. Small. 2008. PMID: 18563746 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Silica-coated CdTe quantum dots functionalized with thiols for bioconjugation to IgG proteins.J Phys Chem B. 2006 Mar 23;110(11):5779-89. doi: 10.1021/jp057435z. J Phys Chem B. 2006. PMID: 16539525
-
Effect of nano-structured polymer surfaces on osteoblast adhesion and proliferation.J Control Release. 2011 Nov 30;152 Suppl 1:e257-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.09.048. J Control Release. 2011. PMID: 22195896 No abstract available.
-
Nanoscale compositional mapping with gentle forces.Nat Mater. 2007 Jun;6(6):405-11. doi: 10.1038/nmat1925. Nat Mater. 2007. PMID: 17541439 Review.
-
Force spectroscopy 101: how to design, perform, and analyze an AFM-based single molecule force spectroscopy experiment.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2011 Oct;15(5):710-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2011.07.020. Epub 2011 Aug 19. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2011. PMID: 21862386 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemotactic synthetic vesicles: Design and applications in blood-brain barrier crossing.Sci Adv. 2017 Aug 2;3(8):e1700362. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1700362. eCollection 2017 Aug. Sci Adv. 2017. PMID: 28782037 Free PMC article.
-
Cell instructive microporous scaffolds through interface engineering.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Dec 12;134(49):20103-9. doi: 10.1021/ja308523f. Epub 2012 Nov 30. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 23163574 Free PMC article.
-
Paclitaxel-Loaded Polymersomes for Enhanced Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Apr;15(4):670-9. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0713-T. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 26880267 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Neutrophilic Inflammation Using Polymersome-Mediated Cellular Delivery.J Immunol. 2017 May 1;198(9):3596-3604. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601901. Epub 2017 Mar 13. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28289157 Free PMC article.
-
Biomolecules Turn Self-Assembling Amphiphilic Block Co-polymer Platforms Into Biomimetic Interfaces.Front Chem. 2019 Jan 8;6:645. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00645. eCollection 2018. Front Chem. 2019. PMID: 30671429 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- LoPresti C, Lomas H, Massignani M, Smart T, Battaglia G. J. Mater. Chem. 2009;19:3576–3590.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

