Comparative evaluation of three automated systems for DNA extraction in conjunction with three commercially available real-time PCR assays for quantitation of plasma Cytomegalovirus DNAemia in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients
- PMID: 21697323
- PMCID: PMC3147763
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00785-11
Comparative evaluation of three automated systems for DNA extraction in conjunction with three commercially available real-time PCR assays for quantitation of plasma Cytomegalovirus DNAemia in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients
Abstract
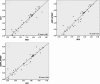
Limited data are available on the performance of different automated extraction platforms and commercially available quantitative real-time PCR (QRT-PCR) methods for the quantitation of cytomegalovirus (CMV) DNA in plasma. We compared the performance characteristics of the Abbott mSample preparation system DNA kit on the m24 SP instrument (Abbott), the High Pure viral nucleic acid kit on the COBAS AmpliPrep system (Roche), and the EZ1 Virus 2.0 kit on the BioRobot EZ1 extraction platform (Qiagen) coupled with the Abbott CMV PCR kit, the LightCycler CMV Quant kit (Roche), and the Q-CMV complete kit (Nanogen), for both plasma specimens from allogeneic stem cell transplant (Allo-SCT) recipients (n = 42) and the OptiQuant CMV DNA panel (AcroMetrix). The EZ1 system displayed the highest extraction efficiency over a wide range of CMV plasma DNA loads, followed by the m24 and the AmpliPrep methods. The Nanogen PCR assay yielded higher mean CMV plasma DNA values than the Abbott and the Roche PCR assays, regardless of the platform used for DNA extraction. Overall, the effects of the extraction method and the QRT-PCR used on CMV plasma DNA load measurements were less pronounced for specimens with high CMV DNA content (>10,000 copies/ml). The performance characteristics of the extraction methods and QRT-PCR assays evaluated herein for clinical samples were extensible at cell-based standards from AcroMetrix. In conclusion, different automated systems are not equally efficient for CMV DNA extraction from plasma specimens, and the plasma CMV DNA loads measured by commercially available QRT-PCRs can differ significantly. The above findings should be taken into consideration for the establishment of cutoff values for the initiation or cessation of preemptive antiviral therapies and for the interpretation of data from clinical studies in the Allo-SCT setting.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differences in cytomegalovirus plasma viral loads measured in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients using two commercial real-time PCR assays.J Clin Virol. 2010 Jun;48(2):142-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2010.03.015. Epub 2010 Apr 14. J Clin Virol. 2010. PMID: 20395168
-
Quantification of cytomegalovirus DNA by a fully automated real-time PCR for early diagnosis and monitoring of active viral infection in solid organ transplant recipients.J Clin Virol. 2013 Feb;56(2):124-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2012.10.015. Epub 2012 Nov 22. J Clin Virol. 2013. PMID: 23182772
-
Impact of automated nucleic acid extraction platforms on plasma Cytomegalovirus DNA loads quantitated by real-time PCR normalized to the 1st WHO international standard.Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin (Engl Ed). 2025 Jan;43(1):28-31. doi: 10.1016/j.eimce.2024.07.007. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin (Engl Ed). 2025. PMID: 39755406
-
Evaluation of COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan CMV Test for use in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2017 Jul;17(7):633-639. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2017.1325737. Epub 2017 May 15. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2017. PMID: 28468570 Review.
-
Quantitative TaqMan assay for the detection and monitoring of cytomegalovirus infection in organ transplant patients.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;335:147-56. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-069-3:147. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16785626 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative evaluation of the QIAsymphony RGQ system with the easyMAG/R-gene combination for the quantitation of cytomegalovirus DNA load in whole blood.Virol J. 2012 Oct 9;9:231. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-231. Virol J. 2012. PMID: 23046712 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary evaluation of the safety and efficacy of standard intravenous immunoglobulins in pregnant women with primary cytomegalovirus infection.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012 Dec;19(12):1991-3. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00509-12. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23100477 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Early kinetics of plasma cytomegalovirus DNA load in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients in the era of highly sensitive real-time PCR assays: does it have any clinical value?J Clin Microbiol. 2014 Feb;52(2):654-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02571-13. Epub 2013 Nov 27. J Clin Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24478505 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical utility of viral load in management of cytomegalovirus infection after solid organ transplantation.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013 Oct;26(4):703-27. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00015-13. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013. PMID: 24092851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of six real-time PCR assays for qualitative detection of cytomegalovirus in clinical specimens.J Clin Microbiol. 2013 Nov;51(11):3749-52. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02005-13. Epub 2013 Sep 4. J Clin Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24006002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbate I., et al. 2008. Evaluation of an automated extraction system in combination with Affigene® CMV Trender for CMV DNA quantitative determination: comparison with nested PCR and pp65 antigen test. J. Virol. Methods 151: 61–65 - PubMed
-
- Allice T., et al. 2008. Evaluation of a novel real-time PCR system for cytomegalovirus DNA quantitation on whole blood and correlation with pp65-antigen test in guiding pre-emptive antiviral treatment. J. Virol. Methods 148: 9–16 - PubMed
-
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. 1986. Statistical method for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet i: 307–310 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

