Attentional templates in visual working memory
- PMID: 21697381
- PMCID: PMC3147306
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1097-11.2011
Attentional templates in visual working memory
Abstract
Most theories of attention propose that we maintain attentional templates in visual working memory to control what information is selected. In the present study, we directly tested this proposal by measuring the contralateral-delay activity (CDA) of human event-related potentials during visual search tasks in which the target is cued on each trial. Here we show that the CDA can be used to measure the maintenance of attentional templates in visual working memory while processing complex visual scenes. In addition, this method allowed us to directly observe the shift from working memory to long-term memory representations controlling attention as learning occurred and experience accrued searching for the same target object. Our findings provide definitive support for several critical proposals made in theories of attention, learning, and automaticity.
Figures
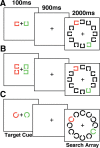
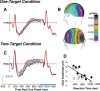
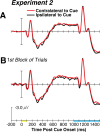
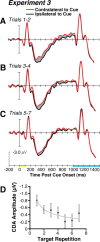
References
-
- Anderson JR. Learning and memory. New York: Wiley; 2000.
-
- Anderson JR. New York: Oxford UP; 2007. How can the human mind occur in the physical universe?
-
- Bundesen C. A theory of visual attention. Psychol Rev. 1990;97:523–547. - PubMed
-
- Bundesen C, Habekost T. New York: Oxford UP; 2008. Principles of visual attention: linking mind and brain.
-
- Bundesen C, Habekost T, Kyllingsbaek S. A neural theory of visual attention: bridging cognition and neurophysiology. Psychol Rev. 2005;112:291–328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
