SIRT1 promotes N-Myc oncogenesis through a positive feedback loop involving the effects of MKP3 and ERK on N-Myc protein stability
- PMID: 21698133
- PMCID: PMC3116909
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002135
SIRT1 promotes N-Myc oncogenesis through a positive feedback loop involving the effects of MKP3 and ERK on N-Myc protein stability
Abstract
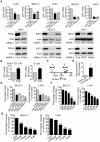
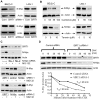
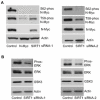
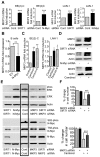
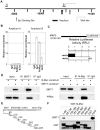
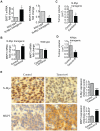
The N-Myc oncoprotein is a critical factor in neuroblastoma tumorigenesis which requires additional mechanisms converting a low-level to a high-level N-Myc expression. N-Myc protein is stabilized when phosphorylated at Serine 62 by phosphorylated ERK protein. Here we describe a novel positive feedback loop whereby N-Myc directly induced the transcription of the class III histone deacetylase SIRT1, which in turn increased N-Myc protein stability. SIRT1 binds to Myc Box I domain of N-Myc protein to form a novel transcriptional repressor complex at gene promoter of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 3 (MKP3), leading to transcriptional repression of MKP3, ERK protein phosphorylation, N-Myc protein phosphorylation at Serine 62, and N-Myc protein stabilization. Importantly, SIRT1 was up-regulated, MKP3 down-regulated, in pre-cancerous cells, and preventative treatment with the SIRT1 inhibitor Cambinol reduced tumorigenesis in TH-MYCN transgenic mice. Our data demonstrate the important roles of SIRT1 in N-Myc oncogenesis and SIRT1 inhibitors in the prevention and therapy of N-Myc-induced neuroblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Brodeur GM. Neuroblastoma: biological insights into a clinical enigma. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:203–216. - PubMed
-
- Maris JM, Matthay KK. Molecular biology of neuroblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2264–2279. - PubMed
-
- Otto T, Horn S, Brockmann M, Eilers U, Schuttrumpf L, et al. Stabilization of N-Myc is a critical function of Aurora A in human neuroblastoma. Cancer Cell. 2009;15:67–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

