Signs of mood and anxiety disorders in chimpanzees
- PMID: 21698223
- PMCID: PMC3116818
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019855
Signs of mood and anxiety disorders in chimpanzees
Abstract
Background: In humans, traumatic experiences are sometimes followed by psychiatric disorders. In chimpanzees, studies have demonstrated an association between traumatic events and the emergence of behavioral disturbances resembling posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and depression. We addressed the following central question: Do chimpanzees develop posttraumatic symptoms, in the form of abnormal behaviors, which cluster into syndromes similar to those described in human mood and anxiety disorders?
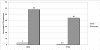
Methodology/principal findings: In phase 1 of this study, we accessed case reports of chimpanzees who had been reportedly subjected to traumatic events, such as maternal separation, social isolation, experimentation, or similar experiences. We applied and tested DSM-IV criteria for PTSD and major depression to published case reports of 20 chimpanzees identified through PrimateLit. Additionally, using the DSM-IV criteria and ethograms as guides, we developed behaviorally anchored alternative criteria that were applied to the case reports. A small number of chimpanzees in the case studies met DSM-IV criteria for PTSD and depression. Measures of inter-rater reliability, including Fleiss' kappa and percentage agreement, were higher with use of the alternative criteria for PTSD and depression. In phase 2, the alternative criteria were applied to chimpanzees living in wild sites in Africa (n = 196) and chimpanzees living in sanctuaries with prior histories of experimentation, orphanage, illegal seizure, or violent human conflict (n = 168). In phase 2, 58% of chimpanzees living in sanctuaries met the set of alternative criteria for depression, compared with 3% of chimpanzees in the wild (p = 0.04), and 44% of chimpanzees in sanctuaries met the set of alternative criteria for PTSD, compared with 0.5% of chimpanzees in the wild (p = 0.04).
Conclusions/significance: Chimpanzees display behavioral clusters similar to PTSD and depression in their key diagnostic criteria, underscoring the importance of ethical considerations regarding the use of chimpanzees in experimentation and other captive settings.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
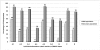
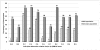
Comment in
-
Assessing the psychological health of captive and wild apes: a response to Ferdowsian et al. (2011).J Comp Psychol. 2013 Aug;127(3):329-36. doi: 10.1037/a0029144. Epub 2012 Aug 13. J Comp Psychol. 2013. PMID: 22889365
-
Mood and anxiety disorders in chimpanzees (pan troglodytes): A response to Rosati et al. (2012).J Comp Psychol. 2013 Aug;127(3):337-40. doi: 10.1037/a0032823. J Comp Psychol. 2013. PMID: 23978231
References
-
- Brent L, Lee DR, Eichberg JW. The effects of single caging on chimpanzee behavior. Lab Anim Sci. 1989;39:345–346. - PubMed
-
- Capitanio JP. Behavioral pathology. In: Erwin MJ, editor. Comparative primate biology, volume 2, part A. Behavior, conservation, and ecology. New York: Alan R. Liss; 1986. pp. 411–454.
-
- Davenport RK, Rogers CM. Differential rearing of the chimpanzee. In: Bourne GH, editor. The chimpanzee, volume 3: Immunology, infection, hormones, anatomy, and behavior. Baltimore: University Park Press; 1970. pp. 337–360.
-
- Goodall J. The chimpanzees of the Gombe: Patterns of behavior. Boston: Harvard University Press; 1986. 673
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

