Rate of progression of hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C: results from the HALT-C Trial
- PMID: 21699796
- PMCID: PMC3773843
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.06.007
Rate of progression of hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C: results from the HALT-C Trial
Abstract
Background & aims: The gradual accumulation of hepatic fibrosis in chronic liver disease results in clinical complications. The rate of hepatic fibrosis score progression (RFSP) in predicting clinical outcomes was assessed by extending the 4-year Hepatitis C Antiviral Long-term Treatment Against Cirrhosis (HALT-C) Trial to include preenrollment liver biopsies.
Methods: The RFSP was calculated from the linear regression slope of Ishak fibrosis score vs time in 457 patients with liver biopsies (≥10-mm length) prior to the HALT-C Trial (575 biopsies) plus 1101 on-study biopsies (total 1676 biopsies). Individual slopes were calculated if duration from first to last biopsy was > 4 years.
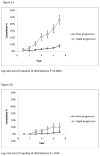
Results: The RFSP as average fibrosis score vs average time in intervals (0-3 and >3 years prestudy, screening, month 24 and 48 on-study) in 455 patients in cohorts of baseline Ishak score ranged from 0.005 with Ishak score 2 to 0.124 with Ishak 6. The RFSP in individual patients (-0.35 to +0.97 Ishak units/year) had a mean of 0.12 ± 0.23 in 344 patients with prestudy and on-study biopsies (group A) and only 0.17 ± 0.22 in 169 with prestudy and screening biopsies (group B). Group A patients with RFSP slope ≥ 0.2 (95 patients, 27.6%) had higher 7-year cumulative rates of non-hepatocellular carcinoma outcomes (46% vs 8%, respectively) and with a hepatocellular carcinoma (10% vs 3%, respectively) than RFSP slope < 02 (249 patients, 72.4%) (P < .0001). RFSP and screening Ishak score correlated independently (P <.0001) with clinical outcomes in multivariate analysis.
Conclusions: Rapid RFSP (>0.2), which occurred in 26.7% of HALT-C Trial patients, correlated strongly with clinical outcomes.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00006164.
Copyright © 2011 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Lawson A, Hagan S, Rye K, et al. The natural history of hepatitis C with severe hepatic fibrosis. J Hepatol. 2007;47:37–45. - PubMed
-
- Poynard T, Bedossa P, Opolon P, et al. Natural history of liver fibrosis progression in patients with chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 1997;345:825–832. - PubMed
-
- Zarski JP, Mc HJ, Bronowicki JP, et al. Rate of natural disease progression in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 2003;38:307–314. - PubMed
-
- D’Amico G, Garcia-Tsao G, Pagliaro L. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: a systematic review of 118 studies. J Hepatol. 2006;44:217–231. - PubMed
-
- Brunt EM. Grading and staging the histopathological lesions of chronic hepatitis: the Knodell histology activity index and beyond. Hepatology. 2000;31:241–246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- N01 DK092320/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 DK092318/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 DK092327/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000065/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000043/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 DK092322/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 DK092328/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 DK092324/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 DK092321/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR006192/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 DK092323/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 DK092326/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000633/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 DK092325/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000827/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 DK092319/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

