Neuronal store-operated calcium entry pathway as a novel therapeutic target for Huntington's disease treatment
- PMID: 21700213
- PMCID: PMC3124661
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2011.04.012
Neuronal store-operated calcium entry pathway as a novel therapeutic target for Huntington's disease treatment
Abstract
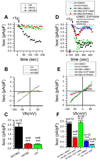
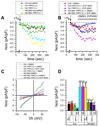
Huntington's disease (HD) is a neurodegenerative disorder caused by a polyglutamine expansion within Huntingtin (Htt) protein. In the phenotypic screen we identified a class of quinazoline-derived compounds that delayed a progression of a motor phenotype in transgenic Drosophila HD flies. We found that the store-operated calcium (Ca(2+)) entry (SOC) pathway activity is enhanced in neuronal cells expressing mutant Htt and that the identified compounds inhibit SOC pathway in HD neurons. The same compounds exerted neuroprotective effects in glutamate-toxicity assays with YAC128 medium spiny neurons primary cultures. We demonstrated a key role of TRPC1 channels in supporting SOC pathway in HD neurons. We concluded that the TRPC1-mediated neuronal SOC pathway constitutes a novel target for HD treatment and that the identified compounds represent a novel class of therapeutic agents for treatment of HD and possibly other neurodegenerative disorders.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Al-Ramahi I, Kim E, SANHUEZA M, DIAZ J, Botas J. Screen of genes involved in Ca2+ homeostasis and signaling to identify genetic modifiers and potential therapeutic targets for Huntington’s Disease treatment. Paper presented at: Society for Neuroscience; San Diego. 2010.
-
- Al-Ramahi I, Lam YC, Chen HK, de Gouyon B, Zhang M, Perez AM, Branco J, de Haro M, Patterson C, Zoghbi HY, et al. CHIP protects from the neurotoxicity of expanded and wild-type ataxin-1 and promotes their ubiquitination and degradation. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:26714–26724. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

