Detecting misery perfusion in unilateral steno-occlusive disease of the internal carotid artery or middle cerebral artery by MR imaging
- PMID: 21700788
- PMCID: PMC7964367
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A2523
Detecting misery perfusion in unilateral steno-occlusive disease of the internal carotid artery or middle cerebral artery by MR imaging
Abstract
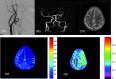
Background and purpose: Elevated OEF is a surrogate for misery perfusion. Our aim was to detect misery perfusion in patients with unilateral steno-occlusive disease of the ICA or MCA by using T2*-based MR imaging and to determine the relationship between brain ischemia and OEF.
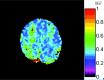
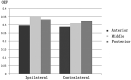
Materials and methods: Twenty-three patients with unilateral steno-occlusive disease of the ICA or MCA and 8 healthy volunteers were included in this study. Hemodynamic information was obtained in all subjects by MR imaging. Three regions of interest were placed in the anterior, middle, and posterior parts of the brain bilaterally to measure the OEF and CBF values. The OEFs of the regions of interest in the hemispheres ipsilateral and contralateral to the vascular lesions were compared. Brain regions with OEF greater than that in controls were determined as misery perfusion in patients. The association of vascular lesions, rCBF, and the presence of territory infarction with elevated OEF was investigated.
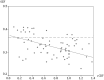
Results: There was a statistically significant difference in OEF between the ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres in the patients (t = 3.632, P = .001). Fourteen regions of interest with misery perfusion were determined in the ipsilateral hemispheres, while 3 regions with elevated OEFs were found in the contralateral hemispheres. In the ipsilateral hemispheres, decreased rCBF was associated with elevated OEF (r = -0.451, P < .001). Patients with territory infarction had more regions of interest with misery perfusion than patients without territory infarction (χ(2) = 3.889, P = .049).
Conclusions: By using the MR imaging technique, misery perfusion demonstrated as elevated OEF was detected in patients with severe atherosclerotic ICA or MCA disease. Identification of misery perfusion with MR imaging may be helpful in the evaluation of brain ischemia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of misery perfusion in the cerebral hemisphere with chronic unilateral major cerebral artery steno-occlusive disease using crossed cerebellar hypoperfusion: comparison of brain SPECT and PET imaging.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013 Oct;40(10):1573-81. doi: 10.1007/s00259-013-2463-2. Epub 2013 Jun 6. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23740375 Free PMC article.
-
Misery perfusion and amyloid deposition in atherosclerotic major cerebral artery disease.Neuroimage Clin. 2019;22:101762. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2019.101762. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Neuroimage Clin. 2019. PMID: 30884364 Free PMC article.
-
Central benzodiazepine receptor binding potential and CBF images on SPECT correlate with oxygen extraction fraction images on PET in the cerebral cortex with unilateral major cerebral artery occlusive disease.J Nucl Med. 2011 Apr;52(4):511-8. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.110.084186. Epub 2011 Mar 18. J Nucl Med. 2011. PMID: 21421729
-
Topographic distribution of misery perfusion in relation to internal and superficial borderzones.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003 Mar;24(3):427-35. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003. PMID: 12637293 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral misery perfusion due to carotid occlusive disease.Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2017 May 18;2(2):88-93. doi: 10.1136/svn-2017-000067. eCollection 2017 Jun. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28959496 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Temporal clustering, tissue composition, and total variation for mapping oxygen extraction fraction using QSM and quantitative BOLD.Magn Reson Med. 2021 Nov;86(5):2635-2646. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28875. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Magn Reson Med. 2021. PMID: 34110656 Free PMC article.
-
Review of the Research Progress of Human Brain Oxygen Extraction Fraction by Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Oct 18;2022:4554271. doi: 10.1155/2022/4554271. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36304964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcranial, Non-Invasive Evaluation of Potential Misery Perfusion During Hyperventilation Therapy of Traumatic Brain Injury Patients.J Neurotrauma. 2023 Oct;40(19-20):2073-2086. doi: 10.1089/neu.2022.0419. Epub 2023 Jun 30. J Neurotrauma. 2023. PMID: 37125452 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging brain oxygenation with MRI using blood oxygenation approaches: methods, validation, and clinical applications.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013 Jun-Jul;34(6):1113-23. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A3070. Epub 2012 Aug 2. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013. PMID: 22859287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cerebral oxygen extraction fraction MRI: Techniques and applications.Magn Reson Med. 2022 Aug;88(2):575-600. doi: 10.1002/mrm.29272. Epub 2022 May 5. Magn Reson Med. 2022. PMID: 35510696 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baron JC, Bousser MG, Rey A, et al. . Reversal of focal “misery perfusion syndrome” by extraintracranial artery bypass in hemodynamic cerebral ischemia: a case study with O15 positron emission tomography. Stroke 1981;12:454–59 - PubMed
-
- Derdeyn CP, Videen TO, Yundt KD, et al. . Variability of cerebral blood volume and oxygen extraction: stages of cerebral haemodynamic impairment revisited. Brain 2002;125 (pt 3):595–607 - PubMed
-
- Powers WJ, Press GA, Grubb RL, Jr, et al. . The effect of hemodynamically significant carotid artery disease on the hemodynamic status of the cerebral circulation. Ann Intern Med 1987;106:27–35 - PubMed
-
- Yamauchi H, Fukuyama H, Nagahama Y, et al. . Significance of increased oxygen extraction fraction in five-year prognosis of major cerebral arterial occlusive diseases. J Nucl Med 1999;40:1992–98 - PubMed
-
- Grubb RL, Jr, Derdeyn CP, Fritsch SM, et al. . The importance of hemodynamic factors in the prognosis of symptomatic carotid occlusion. JAMA 1998;280:1055–60 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
