Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) is required for B-cell tolerance in humans
- PMID: 21700883
- PMCID: PMC3136251
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1102600108
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) is required for B-cell tolerance in humans
Abstract
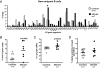
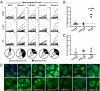
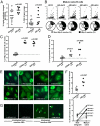
Impaired immune functions leading to primary immunodeficiencies often correlate with paradoxical autoimmune complications; patients with hyper-IgM syndromes who are deficient in activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), which is required for class-switch recombination and somatic hypermutation, are prone to develop autoimmune diseases. To investigate the impact of AID-deficiency on early B-cell tolerance checkpoints in humans, we tested by ELISA the reactivity of recombinant antibodies isolated from single B cells from AID-deficient patients. New emigrant/transitional and mature naive B cells from AID-deficient patients express an abnormal Ig repertoire and high frequencies of autoreactive antibodies, demonstrating that AID is required for the establishment of both central and peripheral B-cell tolerance. In addition, B-cell tolerance was further breached in AID-deficient patients as illustrated by the detection of anti-nuclear IgM antibodies in the serum of all patients. Thus, we identified a major and previously unsuspected role for AID in the removal of developing autoreactive B cells in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
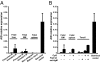
References
-
- Gulino AV, Notarangelo LD. Hyper IgM syndromes. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003;15:422–429. - PubMed
-
- Lee WI, et al. Molecular analysis of a large cohort of patients with the hyper immunoglobulin M (IgM) syndrome. Blood. 2005;105:1881–1890. - PubMed
-
- Muramatsu M, et al. Class switch recombination and hypermutation require activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a potential RNA editing enzyme. Cell. 2000;102:553–563. - PubMed
-
- Revy P, et al. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) deficiency causes the autosomal recessive form of the Hyper-IgM syndrome (HIGM2) Cell. 2000;102:565–575. - PubMed
-
- Imai K, et al. Human uracil-DNA glycosylase deficiency associated with profoundly impaired immunoglobulin class-switch recombination. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:1023–1028. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

