Intrarenal dopamine deficiency leads to hypertension and decreased longevity in mice
- PMID: 21701066
- PMCID: PMC3223841
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI57324
Intrarenal dopamine deficiency leads to hypertension and decreased longevity in mice
Abstract
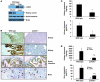
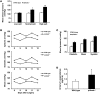
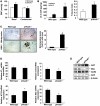
In addition to its role as an essential neurotransmitter, dopamine serves important physiologic functions in organs such as the kidney. Although the kidney synthesizes dopamine through the actions of aromatic amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) in the proximal tubule, previous studies have not discriminated between the roles of extrarenal and intrarenal dopamine in the overall regulation of renal function. To address this issue, we generated mice with selective deletion of AADC in the kidney proximal tubules (referred to herein as ptAadc-/- mice), which led to selective decreases in kidney and urinary dopamine. The ptAadc-/- mice exhibited increased expression of nephron sodium transporters, decreased natriuresis and diuresis in response to l-dihydroxyphenylalanine, and decreased medullary COX-2 expression and urinary prostaglandin E2 excretion and developed salt-sensitive hypertension. They had increased renin expression and altered renal Ang II receptor (AT) expression, with increased AT1b and decreased AT2 and Mas expression, associated with increased renal injury in response to Ang II. They also exhibited a substantially shorter life span compared with that of wild-type mice. These results demonstrate the importance of the intrarenal dopaminergic system in salt and water homeostasis and blood pressure control. Decreasing intrarenal dopamine subjects the kidney to unbuffered responses to Ang II and results in the development of hypertension and a dramatic decrease in longevity.
Figures





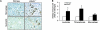

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK51265/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122620/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061018/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK038226/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GM 15431/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- ES 13125/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- DK61018/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM015431/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM015431/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK051265/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK38226/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK62794/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 ES013125/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- DK79341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA122620/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062794/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

