Striatal neuroprotection from neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in piglets by antioxidant treatment with EUK-134 or edaravone
- PMID: 21701140
- PMCID: PMC3225250
- DOI: 10.1159/000327243
Striatal neuroprotection from neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in piglets by antioxidant treatment with EUK-134 or edaravone
Abstract
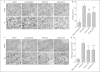
Striatal neurons are highly vulnerable to hypoxia-ischemia (HI) in term newborns. In a piglet model of HI, striatal neurons develop oxidative stress and organelle disruption by 3-6 h of recovery and ischemic cytopathology over 6-24 h of recovery. We tested the hypothesis that early treatment with the antioxidants EUK-134 (a manganese-salen derivative that acts as a scavenger of superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, nitric oxide or NO and peroxynitrite) or edaravone (MCI-186, a scavenger of hydroxyl radical and NO) protects striatal neurons from HI. Anesthetized newborn piglets were subjected to 40 min of hypoxia and 7 min of airway occlusion. At 30 min after resuscitation, the piglets received vehicle, EUK-134 or edaravone. Drug treatment did not affect arterial blood pressure, blood gases, blood glucose or rectal temperature. At 4 days of recovery, the density of viable neurons in the putamen of vehicle-treated piglets was 12 ± 6% (±SD) of sham-operated control density. Treatment with EUK-134 increased viability to 41 ± 17%, and treatment with edaravone increased viability to 39 ± 19%. In the caudate nucleus, neuronal viability was increased from 54 ± 11% in the vehicle group to 78 ± 15% in the EUK-134 group and to 73 ± 13% in the edaravone group. Antioxidant drug treatment accelerated recovery from neurologic deficits and decreased oxidative and nitrative damage to nucleic acids. Treatment with EUK-134 reduced the HI-induced formation of protein carbonyl groups and tyrosine nitration at 3 h of recovery. We conclude that systemic administration of antioxidant agents by 30 min after resuscitation from HI can reduce oxidative stress and salvage neurons in the highly vulnerable striatum in a large-animal model of neonatal HI. Therefore, oxidative stress is an important mechanism for this injury, and antioxidant therapy is a rational, mechanism-based approach to neuroprotection in the newborn brain.
Copyright © 2011 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures





References
-
- Ferriero DM. Neonatal brain injury. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1985–1995. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez FF, Ferriero DM. Therapeutics for neonatal brain injury. Pharmacol Ther. 2008;120:43–53. - PubMed
-
- Ferriero DM. Oxidant mechanisms in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Dev Neurosci. 2001;23:198–202. - PubMed
-
- Lafemina MJ, Sheldon RA, Ferriero DM. Acute hypoxia-ischemia results in hydrogen peroxide accumulation in neonatal but not adult mouse brain. Pediatr Res. 2006;59:680–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

