Revision hip arthroplasty using a cementless modular tapered stem
- PMID: 21701874
- PMCID: PMC3251668
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-011-1299-2
Revision hip arthroplasty using a cementless modular tapered stem
Abstract
Purpose: Here we report the short-term clinical and radiological results of the Profemur®-R cementless modular revision stem.
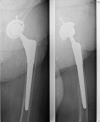
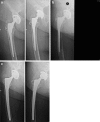
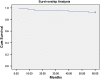
Methods: Between June 2002 and May 2006, 68 revision hip arthroplasties were consecutively performed using this stem. Survival at a mean follow-up of 5.2 years was 94%. According to the Paprosky classification, the femoral defect was classified as type 1 in 39 hips (57.3%), type 2 in 18 hips (26.5%), type 3A in ten hips (14.7%) and type 3B in one hip (1.5%).
Results: The Harris Hip Score was 49.57 before surgery and averaged 78.28 at the latest follow-up. The Merle d'Aubigne score improved from 9.15 preoperatively to 14.30 postoperatively. Stem stability rated according to the Agora Roentgenographic Assessment (ARA) scoring system averaged 5.22, suggesting a high likelihood of a durable implant.
Conclusion: The revision prosthesis examined in this study can be considered a viable and useful option in revision hip arthroplasty, even in patients with bony femoral defects.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cementless total hip arthroplasty with a tapered, rectangular titanium stem and a threaded cup: a minimum ten-year follow-up.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002 Mar;84(3):425-31. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200203000-00014. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002. PMID: 11886913
-
Impaction grafting in the femur in cementless modular revision total hip arthroplasty: a descriptive outcome analysis of 243 cases with the MRP-TITAN revision implant.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013 Jan 11;14:19. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-14-19. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013. PMID: 23311769 Free PMC article.
-
High Survivorship With Cementless Stems and Cortical Strut Allografts for Large Femoral Bone Defects in Revision THA.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015 Sep;473(9):2990-3000. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4358-y. Epub 2015 May 27. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015. PMID: 26013152 Free PMC article.
-
Outcome of a modular tapered uncemented titanium femoral stem in revision hip arthroplasty.Int Orthop. 2015 Sep;39(9):1709-13. doi: 10.1007/s00264-015-2699-5. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Int Orthop. 2015. PMID: 25690924
-
Modular femoral stems for revision total hip arthroplasty.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011 Feb;469(2):476-82. doi: 10.1007/s11999-010-1561-8. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011. PMID: 20865464 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Technical Note for Transfemoral Implantation of Tapered Revision Stems. The Advantage to Stay Short.Arthroplast Today. 2021 Apr 24;9:16-20. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2021.03.015. eCollection 2021 Jun. Arthroplast Today. 2021. PMID: 33997203 Free PMC article.
-
Letter to the Editor: Is There a Benefit to Modularity in 'Simpler' Femoral Revisions?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016 Nov;474(11):2538-2539. doi: 10.1007/s11999-016-4963-4. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016. PMID: 27444030 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Long-term survivorship and complication rate comparison of a cementless modular stem and cementless fixed neck stems for primary total hip replacement.Int Orthop. 2015 Sep;39(9):1827-32. doi: 10.1007/s00264-015-2894-4. Epub 2015 Jul 9. Int Orthop. 2015. PMID: 26156729
-
Monoblock tapered stems in management of UCS B2 and B3 periprosthetic fractures in revision total hip arthroplasty.Bone Jt Open. 2023 Aug 1;4(8):551-558. doi: 10.1302/2633-1462.48.BJO-2022-0160.R1. Bone Jt Open. 2023. PMID: 37524356 Free PMC article.
-
Revision of hip resurfacing arthroplasty with a bone-conserving short-stem implant: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2012 Aug 20;6:249. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-6-249. J Med Case Rep. 2012. PMID: 22905765 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Böhm P, Bischel O. Femoral revision with the Wagner SL revision stem : evaluation of one hundred and twenty-nine revisions followed for a mean of 4.8 years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A(7):1023–1031. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

