Suppression of collagen-induced arthritis in growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein 45β-deficient mice
- PMID: 21702006
- PMCID: PMC3183142
- DOI: 10.1002/art.30497
Suppression of collagen-induced arthritis in growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein 45β-deficient mice
Abstract
Objective: Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein 45β (GADD45β) is involved in stress responses, cell cycle regulation, and oncogenesis. Previous studies demonstrated that GADD45β deficiency exacerbates K/BxN serum-induced arthritis and experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) in mice, indicating that GADD45β plays a suppressive role in innate and adaptive immune responses. To further understand how GADD45β regulates autoimmunity, we evaluated collagen-induced arthritis in GADD45β-/- mice.
Methods: Wild-type (WT) and GADD45β-/- DBA/1 mice were immunized with bovine type II collagen (CII). Serum anticollagen antibody levels were quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Expression of cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases in the joint and spleen was determined by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. The in vitro T cell cytokine response to CII was measured by multiplex analysis. CD4+CD25+ Treg cells and Th17 cells were quantified using flow cytometry.
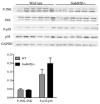
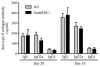
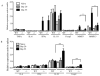
Results: GADD45β-/- mice showed significantly lower arthritis severity and joint destruction compared with WT mice. MMP-3 and MMP-13 expression was also markedly reduced in GADD45β-/- mice. However, serum anti-CII antibody levels were similar in both groups. FoxP3 and interleukin-10 (IL-10) expression was increased 2-3-fold in splenocytes from arthritic GADD45β-/- mice compared with those from WT mice. Flow cytometric analysis showed greater numbers of CD4+CD25+ Treg cells in the spleen of GADD45β-/- mice than in the spleen of WT mice. In vitro studies showed that interferon-γ and IL-17 production by T cells was significantly decreased in GADD45β-/- mice.
Conclusion: Unlike passive K/BxN arthritis and EAE, GADD45β deficiency in CIA was associated with lower arthritis severity, elevated IL-10 expression, decreased IL-17 production, and increased numbers of Treg cells. The data suggest that GADD45β plays a complex role in regulating adaptive immunity and, depending on the model, either enhances or suppresses inflammation.
Copyright © 2011 by the American College of Rheumatology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: none
Figures


Similar articles
-
Decreased collagen-induced arthritis severity and adaptive immunity in MKK-6-deficient mice.Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Mar;64(3):678-87. doi: 10.1002/art.33359. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 21953132 Free PMC article.
-
IL-10 signaling in CD4+ T cells is critical for the pathogenesis of collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(6):R212. doi: 10.1186/ar3545. Epub 2011 Dec 22. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011. PMID: 22192790 Free PMC article.
-
Gadd45beta deficiency in rheumatoid arthritis: enhanced synovitis through JNK signaling.Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Nov;60(11):3229-40. doi: 10.1002/art.24887. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 19877043 Free PMC article.
-
Rebamipide suppresses collagen-induced arthritis through reciprocal regulation of th17/treg cell differentiation and heme oxygenase 1 induction.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014 Apr;66(4):874-85. doi: 10.1002/art.38310. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24757140
-
Intervention of Tyrosine Hydroxylase Expression Alters Joint Inflammation and Th17/Treg Imbalance in Collagen-Induced Arthritis.Neurosignals. 2021 Feb 6;29(1):1-13. doi: 10.33594/000000328. Neurosignals. 2021. PMID: 33547770
Cited by
-
Preclinical toxicology and safety pharmacology of the first-in-class GADD45β/MKK7 inhibitor and clinical candidate, DTP3.Toxicol Rep. 2019 Apr 19;6:369-379. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.04.006. eCollection 2019. Toxicol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31080744 Free PMC article.
-
Duality of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in RA: passive responders and imprinted aggressors.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013 Jan;9(1):24-33. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2012.190. Epub 2012 Nov 13. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23147896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible 45: a new player on inflammatory diseases.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 27;16:1513069. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1513069. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40083548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long Non-coding RNA FENDRR Acts as a miR-423-5p Sponge to Suppress the Treg-Mediated Immune Escape of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019 Sep 6;17:516-529. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.05.027. Epub 2019 Jun 12. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019. PMID: 31351327 Free PMC article.
-
Euphorbia Factor L2 ameliorates the Progression of K/BxN Serum-Induced Arthritis by Blocking TLR7 Mediated IRAK4/IKKβ/IRF5 and NF-kB Signaling Pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 3;12:773592. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.773592. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34950033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423:356–61. - PubMed
-
- Sondergaard BC, Schultz N, Madsen SH, Bay-Jensen AC, Kassem M, Karsdal MA. MAPKs are essential upstream signaling pathways in proteolytic cartilage degradation--divergence in pathways leading to aggrecanase and MMP-mediated articular cartilage degradation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18:279–88. - PubMed
-
- Thalhamer T, McGrath MA, Harnett MM. MAPKs and their relevance to arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008;47:409–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

