A phase III randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of pilocarpine for vaginal dryness: North Central Cancer Treatment group study N04CA
- PMID: 21702402
- PMCID: PMC3141345
- DOI: 10.1016/j.suponc.2011.02.005
A phase III randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of pilocarpine for vaginal dryness: North Central Cancer Treatment group study N04CA
Abstract
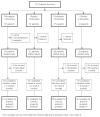
Vaginal dryness is a common problem for which effective and safe nonestrogenic treatments are needed. Based on preliminary promising data that pilocarpine attenuated vaginal dryness, the current trial was conducted. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial design was used to compare pilocarpine, at target doses of 5 mg twice daily and 5 mg four times daily, with a placebo. Vaginal dryness was recorded by patient-completed questionnaires at baseline and weekly for 6 weeks after study initiation. The primary endpoint for this study was the area under the curve summary statistic composed of the longitudinal responses obtained at baseline and through the 6 weeks of treatment to a numerical analogue scale asking patients to rate their perceived amount of vaginal dryness. The primary analysis was carried out by a single t test using a two-side alternative to compare the collective pilocarpine treatment arms with the collective placebo arms. A total of 201 patients enrolled in this trial. The primary analysis, comparing vaginal dryness symptoms in the collective pilocarpine arms against the placebo arm, did not reveal any benefit for the pilocarpine treatment. This finding was confirmed by other secondary analyses. Toxicity evaluation revealed more nausea, sweating, rigors, and urinary frequency with the pilocarpine arms compared with the placebo arm.
Figures
References
-
- Pastore LM, Carter RA, Hulka BS, Wells E. Self-reported urogenital symptoms in postmenopausal women: Women's Health Initiative. Maturitas. 2004;49(4):292–303. - PubMed
-
- Dennerstein L, Dudley EC, Hopper JL, Guthrie JR, Burger HG. A prospective population-based study of menopausal symptoms. Obstet Gynecol. 2000;96(3):351–8. - PubMed
-
- Ganz PA, Greendale GA, Petersen L, Zibecchi L, Kahn B, Belin TR. Managing menopausal symptoms in breast cancer survivors: results of a randomized controlled trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92(13):1054–64. - PubMed
-
- Knobf MT. The menopausal symptom experience in young mid-life women with breast cancer. Cancer Nurs. 2001;24(3):201–10. quiz 10–1. - PubMed
-
- Leclair DM, Anandarajah G. Effects of Estrogen Deprivation: Vasomotor Symptoms, Urogenital Atrophy, and Psychobiologic Effects. Menopause (New York, NY) 2002;4(1):27–39.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10 CA035267/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA052352/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-52352/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-25224/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35269/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA025224/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035269/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-37404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063848/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-63848/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063849/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-37417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35267/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-63849/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical