Induced elastic matrix deposition within three-dimensional collagen scaffolds
- PMID: 21702719
- PMCID: PMC3204196
- DOI: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2010.0749
Induced elastic matrix deposition within three-dimensional collagen scaffolds
Abstract
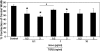
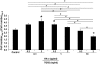
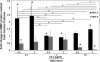
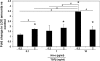
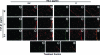
The structural stability of a cyclically distending elastic artery and the healthy functioning of vascular smooth muscle cells (SMCs) within are maintained by the presence of an intact elastic matrix and its principal protein, elastin. The accelerated degradation of the elastic matrix, which occurs in several vascular diseases, coupled with the poor ability of adult SMCs to regenerate lost elastin, can therefore adversely impact vascular homeostasis. Similarly, efforts to tissue engineer elastic matrix structures are constrained by our inability to induce adult cells to synthesize tropoelastin precursors and to crosslink them into architectural mimics of native elastic matrices, especially within engineered constructs where SMCs/fibroblasts primarily deposit collagen in abundance. In this study, we have shown that transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-β1) and hyaluronan oligomers (HA-o) synergistically enhance elastic matrix deposition by adult rat aortic SMCs (RASMCs) seeded within nonelastogenic, statically loaded three-dimensional gels, composed of nonelastogenic type-I collagen. While there was no substantial increase in production of tropoelastin within experimental cases compared to the nonadditive control cultures over 3 weeks, we observed significant increases in matrix elastin deposition; soluble matrix elastin in constructs that received the lowest doses of TGF-β1 with respective doses of HA-o, and insoluble matrix at the highest doses that corresponded with elevated lysyl-oxidase protein quantities. However, despite elastogenic induction, overall matrix yields remained poor in all experimental cases. At all provided doses, the factors reduced the production of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-9, especially the active enzyme, though MMP-2 levels were lowered only in constructs cultured with the higher doses of TGF-β1. Immuno-fluorescence showed elastic fibers within the collagen constructs to be discontinuous, except at the edges of the constructs. Von Kossa staining revealed no calcific deposits in any of the cases. This study confirms the benefits of utilizing TGF-β1 and HA-o in inducing matrix elastin synthesis by adult RASMCs over nonadditive controls, within a collagenous environment, that is not inherently conducive to elastogenesis.
Figures

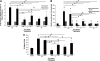



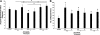

Similar articles
-
Elastogenic inductability of smooth muscle cells from a rat model of late stage abdominal aortic aneurysms.Tissue Eng Part A. 2011 Jul;17(13-14):1699-711. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2010.0526. Epub 2011 May 9. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011. PMID: 21341992 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of hyaluronan oligomers and transforming growth factor-beta1 factors for elastic matrix regeneration by aneurysmal rat aortic smooth muscle cells.Tissue Eng Part A. 2009 Nov;15(11):3247-60. doi: 10.1089/ten.tea.2008.0593. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009. PMID: 19374489 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of pre-existing elastic matrix on TGFβ1 and HA oligomer-induced regenerative elastin repair by rat aortic smooth muscle cells.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2011 Feb;5(2):85-96. doi: 10.1002/term.286. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2011. PMID: 20653044 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue engineering and regenerative strategies to replicate biocomplexity of vascular elastic matrix assembly.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2012 Jun;18(3):203-17. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2011.0521. Epub 2012 Mar 2. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2012. PMID: 22224468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of the Stromal Extracellular Matrix in the Development of Pterygium Pathology: An Update.J Clin Med. 2021 Dec 17;10(24):5930. doi: 10.3390/jcm10245930. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34945227 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Chronic Stress and Exercise on Microvascular Function in Metabolic Syndrome.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018 May;50(5):957-966. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000001531. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018. PMID: 29271845 Free PMC article.
-
Biological and engineering design considerations for vascular tissue engineered blood vessels (TEBVs).Curr Opin Chem Eng. 2014 Feb 1;3:83-90. doi: 10.1016/j.coche.2013.12.001. Curr Opin Chem Eng. 2014. PMID: 24511460 Free PMC article.
-
Induced Regenerative Elastic Matrix Repair in LOXL1 Knockout Mouse Cell Cultures: Towards Potential therapy for Pelvic Organ Prolapse.J Tissue Sci Eng. 2012;3(3):120. doi: 10.4172/2157-7552.1000120. Epub 2012 Sep 28. J Tissue Sci Eng. 2012. PMID: 30854248 Free PMC article.
-
Cathepsin K-targeted sub-micron particles for regenerative repair of vascular elastic matrix.Acta Biomater. 2017 Apr 1;52:60-73. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.01.032. Epub 2017 Jan 10. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28087488 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional nanoparticles for doxycycline delivery towards localized elastic matrix stabilization and regenerative repair.Acta Biomater. 2013 May;9(5):6511-25. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2013.01.023. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Acta Biomater. 2013. PMID: 23376127 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosenbloom J. Abrams W.R. Mecham R. Extracellular matrix 4: the elastic fiber. FASEB J. 1993;7:1208. - PubMed
-
- Rodgers U.R. Weiss A.S. Cellular interactions with elastin. Pathol Biol. 2005;53:390. - PubMed
-
- Li D.Y. Brooke B. Davis E.C. Mecham R.P. Sorensen L.K. Boak B.B. Eichwald E. Keating M.T. Elastin is an essential determinant of arterial morphogenesis. Nature. 1998;393:276. - PubMed
-
- Patel A. Fine B. Sandig M. Mequanint K. Elastin biosynthesis: the missing link in tissue-engineered blood vessels. Cardiovasc Res. 2006;71:40. - PubMed
-
- Thie M. Schlumberger W. Semich R. Rauterberg J. Robenek H. Aortic smooth muscle cells in collagen lattice culture: effects on ultrastructure, proliferation and collagen synthesis. Eur J Cell Biol. 1991;55:295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

