Lymph node-derived donor encephalitogenic CD4+ T cells in C57BL/6 mice adoptive transfer experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis highly express GM-CSF and T-bet
- PMID: 21702922
- PMCID: PMC3161869
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-73
Lymph node-derived donor encephalitogenic CD4+ T cells in C57BL/6 mice adoptive transfer experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis highly express GM-CSF and T-bet
Abstract
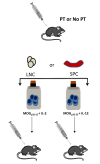
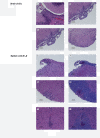
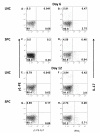
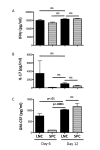
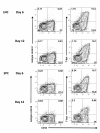
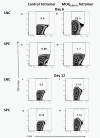
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is a relevant animal model for the human demyelinating inflammatory disorder of the central nervous system (CNS), multiple sclerosis (MS). Induction of EAE by adoptive transfer allows studying the role of the donor T lymphocyte in disease pathogenesis. It has been challenging to reliably induce adoptive transfer EAE in C57BL/6 (H-2b) mice. The goal of this study was to develop a reproducible and high yield protocol for adoptive transfer EAE in C57BL/6 mice. A step-wise experimental approach permitted us to develop a protocol that resulted in a consistent relatively high disease incidence of ~70% in recipient mice. Donor mice were immunized with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG)p35-55 in complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) followed by pertussis toxin (PT). Only lymph node cells (LNC) isolated at day 12 post immunization, and restimulated in vitro for 72 hours with 10 μg/mL of MOGp35-55 and 0.5 ng/mL of interleukin-12 (IL-12) were able to transfer disease. The ability of LNC to transfer disease was associated with the presence of inflammatory infiltrates in the CNS at day 12. Interferon gamma (IFNγ) was produced at comparable levels in cell cultures prepared from mice at both day 6 and day 12 post immunization. By contrast, there was a trend towards a negative association between IL-17 and disease susceptibility in our EAE model. The amount of GM-CSF secreted was significantly increased in the culture supernatants from cells collected at day 12 post immunization versus those collected at day 6 post-immunization. Activated CD4+ T cells present in the day 12 LNC cultures maintained expression of the transcription factor T-bet, which has been shown to regulate the expression of the IL-23 receptor. Also, there was an increased prevalence of MOGp35-55-specific CD4+ T cells in day 12 LNC after in vitro re-stimulation. In summary, encephalitogenic LNC that adoptively transfer EAE in C57BL/6 mice were not characterized by a single biomarker in our study, but by a composite of inflammatory markers. Our data further suggest that GM-CSF expression by CD4+ T cells regulated by IL-23 contributes to their encephalitogenicity in our EAE model.
Figures

Similar articles
-
GM-CSF Promotes Chronic Disability in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Altering the Composition of Central Nervous System-Infiltrating Cells, but Is Dispensable for Disease Induction.J Immunol. 2018 Feb 1;200(3):966-973. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701484. Epub 2017 Dec 29. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29288202 Free PMC article.
-
T cell-depleted splenocytes from mice pre-immunized with neuroantigen in incomplete Freund's adjuvant involved in protection from experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Immunol Lett. 2014 Jan-Feb;157(1-2):38-44. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2013.11.001. Epub 2013 Nov 9. Immunol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24220208
-
Host T cells are the main producers of IL-17 within the central nervous system during initiation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis induced by adoptive transfer of Th1 cell lines.J Immunol. 2008 Jun 15;180(12):8066-72. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.12.8066. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18523270
-
Control of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by CD4+ suppressor T cells: peripheral versus in situ immunoregulation.J Neuroimmunol. 2007 Nov;191(1-2):61-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2007.09.010. Epub 2007 Sep 27. J Neuroimmunol. 2007. PMID: 17900707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using EAE to better understand principles of immune function and autoimmune pathology.J Autoimmun. 2013 Sep;45:31-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2013.06.008. Epub 2013 Jul 9. J Autoimmun. 2013. PMID: 23849779 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Blood coagulation factor XII drives adaptive immunity during neuroinflammation via CD87-mediated modulation of dendritic cells.Nat Commun. 2016 May 18;7:11626. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11626. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27188843 Free PMC article.
-
Th40 cells (CD4+CD40+ Tcells) drive a more severe form of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis than conventional CD4 T cells.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 13;12(2):e0172037. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172037. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28192476 Free PMC article.
-
Human aquaporin 4281-300 is the immunodominant linear determinant in the context of HLA-DRB1*03:01: relevance for diagnosing and monitoring patients with neuromyelitis optica.Arch Neurol. 2012 Sep;69(9):1125-31. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2012.1300. Arch Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22751865 Free PMC article.
-
Smad7 in intestinal CD4+ T cells determines autoimmunity in a spontaneous model of multiple sclerosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Dec 17;116(51):25860-25869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1905955116. Epub 2019 Dec 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31796589 Free PMC article.
-
Dihydroartemisinin Regulates the Th/Treg Balance by Inducing Activated CD4+ T cell Apoptosis via Heme Oxygenase-1 Induction in Mouse Models of Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Molecules. 2019 Jul 5;24(13):2475. doi: 10.3390/molecules24132475. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31284478 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

