Role of the SaeRS two-component regulatory system in Staphylococcus epidermidis autolysis and biofilm formation
- PMID: 21702925
- PMCID: PMC3224141
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-146
Role of the SaeRS two-component regulatory system in Staphylococcus epidermidis autolysis and biofilm formation
Abstract
Background: Staphylococcus epidermidis (SE) has emerged as one of the most important causes of nosocomial infections. The SaeRS two-component signal transduction system (TCS) influences virulence and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus. The deletion of saeR in S. epidermidis results in impaired anaerobic growth and decreased nitrate utilization. However, the regulatory function of SaeRS on biofilm formation and autolysis in S. epidermidis remains unclear.
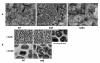
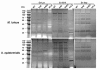
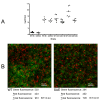
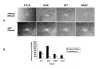
Results: The saeRS genes of SE1457 were deleted by homologous recombination. The saeRS deletion mutant, SE1457ΔsaeRS, exhibited increased biofilm formation that was disturbed more severely (a 4-fold reduction) by DNase I treatment compared to SE1457 and the complementation strain SE1457saec. Compared to SE1457 and SE1457saec, SE1457ΔsaeRS showed increased Triton X-100-induced autolysis (approximately 3-fold) and decreased cell viability in planktonic/biofilm states; further, SE1457ΔsaeRS also released more extracellular DNA (eDNA) in the biofilms. Correlated with the increased autolysis phenotype, the transcription of autolysis-related genes, such as atlE and aae, was increased in SE1457ΔsaeRS. Whereas the expression of accumulation-associated protein was up-regulated by 1.8-fold in 1457ΔsaeRS, the expression of an N-acetylglucosaminyl transferase enzyme (encoded by icaA) critical for polysaccharide intercellular adhesin (PIA) synthesis was not affected by the deletion of saeRS.
Conclusions: Deletion of saeRS in S. epidermidis resulted in an increase in biofilm-forming ability, which was associated with increased eDNA release and up-regulated Aap expression. The increased eDNA release from SE1457ΔsaeRS was associated with increased bacterial autolysis and decreased bacterial cell viability in the planktonic/biofilm states.
Figures
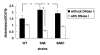

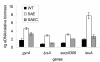
Similar articles
-
sarA negatively regulates Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation by modulating expression of 1 MDa extracellular matrix binding protein and autolysis-dependent release of eDNA.Mol Microbiol. 2012 Oct;86(2):394-410. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08203.x. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Mol Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22957858
-
The Vancomycin Resistance-Associated Regulatory System VraSR Modulates Biofilm Formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis in an ica-Dependent Manner.mSphere. 2021 Oct 27;6(5):e0064121. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00641-21. Epub 2021 Sep 22. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34550006 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotine Enhances Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm Formation by Altering the Bacterial Autolysis, Extracellular DNA Releasing, and Polysaccharide Intercellular Adhesin Production.Front Microbiol. 2018 Oct 29;9:2575. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02575. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30420846 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharide intercellular adhesin in biofilm: structural and regulatory aspects.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Feb 10;5:7. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00007. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25713785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ica and beyond: biofilm mechanisms and regulation in Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007 May;270(2):179-88. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00688.x. Epub 2007 Apr 10. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007. PMID: 17419768 Review.
Cited by
-
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of the DNA-binding domain of the response regulator SaeR from Staphylococcus epidermidis.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2013 Jun;69(Pt 6):689-91. doi: 10.1107/S1744309113012943. Epub 2013 May 25. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2013. PMID: 23722855 Free PMC article.
-
Monoclonal Antibodies Specific to the Extracellular Domain of Histidine Kinase YycG of Staphylococcus epidermidis Inhibit Biofilm Formation.Front Microbiol. 2020 Aug 7;11:1839. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01839. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32849437 Free PMC article.
-
MrSkn7 controls sporulation, cell wall integrity, autolysis, and virulence in Metarhizium robertsii.Eukaryot Cell. 2015 Apr;14(4):396-405. doi: 10.1128/EC.00266-14. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Eukaryot Cell. 2015. PMID: 25710964 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Seq analysis of differentially expressed genes of Staphylococcus epidermidis isolated from postoperative endophthalmitis and the healthy conjunctiva.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 28;10(1):14234. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71050-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32859978 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Holy Triangle of Quorum Sensing, Biofilm Formation, and Antibiotic Resistance in Pathogenic Bacteria.Microorganisms. 2022 Jun 16;10(6):1239. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10061239. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35744757 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rohde H, Bartscht K, Hussain M, Buck F, Horstkotte MA, Knobloch JKM, Heilmann C, Herrmann M, Mack D. The repetitive domain B of the accumulation associated protein Aap mediates intercellular adhesion and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus epidermidis. Int J Med Microbiol. 2004;294:128–128.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

