Exploring internal features of 16S rRNA gene for identification of clinically relevant species of the genus Streptococcus
- PMID: 21702978
- PMCID: PMC3151204
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-0711-10-28
Exploring internal features of 16S rRNA gene for identification of clinically relevant species of the genus Streptococcus
Abstract
Background: Streptococcus is an economically important genus as a number of species belonging to this genus are human and animal pathogens. The genus has been divided into different groups based on 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity. The variability observed among the members of these groups is low and it is difficult to distinguish them. The present study was taken up to explore 16S rRNA gene sequence to develop methods that can be used for preliminary identification and can supplement the existing methods for identification of clinically-relevant isolates of the genus Streptococcus.
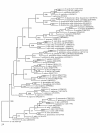
Methods: 16S rRNA gene sequences belonging to the isolates of S. dysgalactiae, S. equi, S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. bovis, S. gallolyticus, S. mutans, S. sobrinus, S. mitis, S. pneumoniae, S. thermophilus and S. anginosus were analyzed with the purpose to define genetic variability within each species to generate a phylogenetic framework, to identify species-specific signatures and in-silico restriction enzyme analysis.
Results: The framework based analysis was used to segregate Streptococcus spp. previously identified upto genus level. This segregation was validated using species-specific signatures and in-silico restriction enzyme analysis. 43 uncharacterized Streptococcus spp. could be identified using this approach.
Conclusions: The markers generated exploring 16S rRNA gene sequences provided useful tool that can be further used for identification of different species of the genus Streptococcus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Delineation of Streptococcus dysgalactiae, its subspecies, and its clinical and phylogenetic relationship to Streptococcus pyogenes.J Clin Microbiol. 2012 Jan;50(1):113-26. doi: 10.1128/JCM.05900-11. Epub 2011 Nov 9. J Clin Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22075580 Free PMC article.
-
Partial recN gene sequencing: a new tool for identification and phylogeny within the genus Streptococcus.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2010 Sep;60(Pt 9):2140-2148. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.018176-0. Epub 2009 Oct 30. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 19880633
-
Determination of 16S rRNA sequences of Streptococcus mitis and Streptococcus gordonii and phylogenetic relationships among members of the genus Streptococcus.Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1995 Apr;45(2):406-8. doi: 10.1099/00207713-45-2-406. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1995. PMID: 7537076
-
Genetic approaches to the identification of the mitis group within the genus Streptococcus.Microbiology (Reading). 1999 Sep;145 ( Pt 9):2605-2613. doi: 10.1099/00221287-145-9-2605. Microbiology (Reading). 1999. PMID: 10517614
-
Identification of alpha-hemolytic streptococci by pyrosequencing the 16S rRNA gene and by use of VITEK 2.J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Mar;45(3):762-70. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01342-06. Epub 2007 Jan 10. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17215341 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
An In Silico Approach for Identification of the Pathogenic Species, Helicobacter pylori and Its Relatives.Indian J Microbiol. 2016 Sep;56(3):277-86. doi: 10.1007/s12088-016-0575-7. Epub 2016 Apr 30. Indian J Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27407291 Free PMC article.
-
Species-level bacterial community profiling of the healthy sinonasal microbiome using Pacific Biosciences sequencing of full-length 16S rRNA genes.Microbiome. 2018 Oct 23;6(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0569-2. Microbiome. 2018. PMID: 30352611 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and molecular identification of Gram-positive isolates with β-hemolysis activity isolated from the nasal swab of pigs during the human meningitis outbreak in Badung Regency, Bali-Indonesia.Vet World. 2022 Jan;15(1):140-146. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2022.140-146. Epub 2022 Jan 25. Vet World. 2022. PMID: 35369582 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparison of Three Different Bioinformatics Analyses of the 16S-23S rRNA Encoding Region for Bacterial Identification.Front Microbiol. 2019 Apr 16;10:620. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00620. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31040829 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the efficiency of 16S-ITS-23S operon sequencing for species level resolution in microbial communities.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 22;15(1):2822. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83410-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39843557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ryan KJ, Ray CG. Sherris Medical Microbiology. 4. McGraw Hill; 2004.
-
- Hardie JM, Whiley RA. In: The Genera of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Wood BJB, Holz-apfel WH, editor. Vol. 2. Blackie Academic and Professional; 1995. The genus Streptococcus; pp. 55–124.
-
- Wilson CD, Salt GFH. In: Streptococci. Society for Applied Bacteriology Symposium Series No. 7. Skinner FA, Quesnel LB, editor. London, New York, San Francisco: Academic Press; 1978. Streptococci in animal disease; pp. 143–156. - PubMed
-
- Farrow JAE, Collins MD. Taxonomic studies on streptococci of serological groups C, G and L and possibly related taxa. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1984;5:483–493.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

