Ischemic cardiomyopathy following seizure induction by domoic Acid
- PMID: 21703399
- PMCID: PMC3123868
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.03.017
Ischemic cardiomyopathy following seizure induction by domoic Acid
Abstract
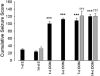
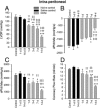
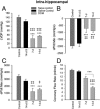
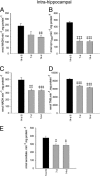
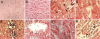
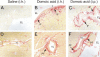
Exposure to the excitotoxin domoic acid (DOM) has been shown to produce cardiac lesions in both clinical and animal studies. We have previously shown that DOM failed to directly affect cardiomyocyte viability and energetics, but the development of this cardiomyopathy has remained unexplained. The present study compared effects of high-level seizure induction obtained by intraperitoneal (2 mg/kg) or intrahippocampal (100 pmol) bolus administration of DOM on development of cardiac pathologies in a rat model. Assessment of cardiac pressure derivatives and coronary flow rates revealed a significant time-dependent decrease in combined left ventricular (LV) systolic and diastolic function at 1, 3, 7, and 14 days after intraperitoneal administration and at 7 and 14 days after intrahippocampal DOM administration. LV dysfunction was matched by a similar time-dependent decrease in mitochondrial respiratory control, associated with increased proton leakage, and in mitochondrial enzyme activities. Microscopic examination of the LV midplane revealed evidence of progressive multifocal ischemic damage within the subendocardial, septal, and papillary regions. Lesions ranged from reversible early damage (vacuolization) to hypercontracture and inflammatory necrosis progressing to fibrotic scarring. Plasma proinflammatory IL-1α, IL-1β, and TNF-α cytokine levels were also increased from 3 days after seizure induction. The observed cardiomyopathies did not differ between intraperitoneal and intrahippocampal groups, providing strong evidence that cardiac damage after DOM exposure is a consequence of a seizure-evoked autonomic response.
Copyright © 2011 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


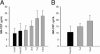
Similar articles
-
Neonatal exposure to low-dose domoic acid lowers seizure threshold in adult rats.Neuroscience. 2010 Sep 15;169(4):1789-99. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.06.045. Epub 2010 Jun 25. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20600646
-
Systemic administration of domoic acid-induced spinal cord lesions in neonatal rats.J Spinal Cord Med. 2000 Spring;23(1):31-9. doi: 10.1080/10790268.2000.11753506. J Spinal Cord Med. 2000. PMID: 10752872
-
Domoic acid preconditioning and seizure induction in young and aged rats.Epilepsy Res. 2007 Sep;76(2-3):103-12. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2007.07.003. Epub 2007 Aug 22. Epilepsy Res. 2007. PMID: 17716870
-
Neuropathology of excitatory neurotoxins: the domoic acid model.Toxicol Pathol. 1990;18(1 Pt 2):165-9. doi: 10.1177/019262339001800122. Toxicol Pathol. 1990. PMID: 2195636 Review.
-
Perinatal Domoic Acid as a Neuroteratogen.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2016;29:87-110. doi: 10.1007/7854_2015_417. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26695171 Review.
Cited by
-
The Toxic Effects of Environmental Domoic Acid Exposure on Humans and Marine Wildlife.Mar Drugs. 2025 Jan 29;23(2):61. doi: 10.3390/md23020061. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39997185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How Safe Is Safe for Marine Toxins Monitoring?Toxins (Basel). 2016 Jul 6;8(7):208. doi: 10.3390/toxins8070208. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27399774 Free PMC article.
-
Modulatory effects of Terminalia arjuna against domoic acid induced toxicity in Caco-2 cell line.Cytotechnology. 2017 Aug;69(4):725-739. doi: 10.1007/s10616-017-0080-9. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Cytotechnology. 2017. PMID: 28342004 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of renal toxicity in mice administered the marine biotoxin domoic Acid.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 Jun;25(6):1187-97. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013080836. Epub 2014 Feb 8. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24511141 Free PMC article.
-
Mitophagy as a mitochondrial quality control mechanism in myocardial ischemic stress: from bench to bedside.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023 May;28(3):239-251. doi: 10.1007/s12192-023-01346-9. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023. PMID: 37093549 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Perl T.M., Bédard L., Kosatsky T., Hockin J.C., Todd E.C.D., Remis R.S. An outbreak of toxic encephalopathy caused by eating mussels contaminated with domoic acid. N Engl J Med. 1990;322:1775–1780. - PubMed
-
- Teitelbaum J., Carpenter S., Cashman N.R. Neurologic sequelae after ingestion of mussels contaminated with domoic acid. N Engl J Med. 1990;323:1632–1633. - PubMed
-
- Lefebvre K.A., Bargu S., Kieckhefer T., Silver M.W. From sanddabs to blue whales: the pervasiveness of domoic acid. Toxicon. 2002;40:971–977. - PubMed
-
- Scallet A.C., Schmued L.C., Johannessen J.N. Neurohistochemical biomarkers of the marine neurotoxicant, domoic acid. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2005;27:745–752. - PubMed
-
- Cendes F., Andermann F., Carpenter S., Zatorre R.J., Cashman N.R. Temporal lobe epilepsy caused by domoic acid intoxication: evidence for glutamate receptor-mediated excitotoxicity in humans. Ann Neurol. 1995;37:123–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

