Increased serum enzyme levels associated with kupffer cell reduction with no signs of hepatic or skeletal muscle injury
- PMID: 21703406
- PMCID: PMC3123844
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.03.029
Increased serum enzyme levels associated with kupffer cell reduction with no signs of hepatic or skeletal muscle injury
Abstract
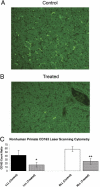
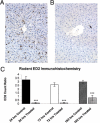
Macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) is a hematopoietic growth factor that is responsible for the survival and proliferation of monocytes and the differentiation of monocytes into macrophages, including Kupffer cells (KCs) in the liver. KCs play an important role in the clearance of several serum enzymes, including aspartate aminotransferase and creatine kinase, that are typically elevated as a result of liver or skeletal muscle injury. We used three distinct animal models to investigate the hypothesis that increases in the levels of serum enzymes can be the result of decreases in KCs in the apparent absence of hepatic or skeletal muscle injury. Specifically, neutralizing M-CSF activity via a novel human monoclonal antibody reduced the CD14(+)CD16(+) monocyte population, depleted KCs, and increased aspartate aminotransferase and creatine kinase serum enzyme levels in cynomolgus macaques. In addition, the treatment of rats with clodronate liposomes depleted KCs and led to increased serum enzyme levels, again without evidence of tissue injury. Finally, in the osteopetrotic (Csf1(op)/Csf1(op)) mice lacking functional M-CSF and having reduced levels of KCs, the levels of serum enzymes are higher than in wild-type littermates. Together, these findings support a mechanism for increases in serum enzyme levels through M-CSF regulation of tissue macrophage homeostasis without concomitant histopathological changes in either the hepatic or skeletal system.
Copyright © 2011 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Naito M., Hasegawa G., Ebe Y., Yamamoto T. Differentiation and function of Kupffer cells. Med Electron Microsc. 2004;37:16–28. - PubMed
-
- Charlier N., Neyrinck A.M., Beghein N., Delzenne N.M., Gallez B. Assessment of liver phagocytic activity using EPR spectrometry and imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;27:565–569. - PubMed
-
- Helmy K.Y., Katschke K.J., Jr, Gorgani N.N., Kljavin N.M., Elliott J.M., Diehl L., Scales S.J., Ghilardi N., van Lookeren Campagne M. CRIg: a macrophage complement receptor required for phagocytosis of circulating pathogens. Cell. 2006;124:915–927. - PubMed
-
- Toth C.A., Thomas P. Liver endocytosis and Kupffer cells. Hepatology. 1992;16:255–266. - PubMed
-
- Granado M., Martín A.I., Priego T., Villanúa M.A., López-Calderón A. Inactivation of Kupffer cells by gadolinium administration prevent lipopolysaccharide-induced decrease in liver insulin-like growth factor-I and IGF-binding protein-3 gene expression. J Endocrinol. 2006;188:503–511. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

