Expression and regulation of the ΔN and TAp63 isoforms in salivary gland tumorigenesis clinical and experimental findings
- PMID: 21703418
- PMCID: PMC3123859
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.03.037
Expression and regulation of the ΔN and TAp63 isoforms in salivary gland tumorigenesis clinical and experimental findings
Abstract
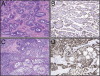
The TP63 gene, a TP53 homologue, encodes for two main isoforms by different promoters: one retains (TA) and the other lacks (ΔN) the transactivation domain. p63 plays a critical role in the maintenance of basal and myoepithelial cells in ectodermally derived tissues and is implicated in tumorigenesis of several neoplastic entities. However, the biological and regulatory roles of these isoforms in salivary gland tumorigenesis remain unknown. Our results show a reciprocal expression between TA and ΔN isoforms in both benign and malignant salivary tumors. The most dominantly expressed were the ΔN isoforms, whereas the TA isoforms showed generally low levels of expression, except in a few tumors. High ΔNp63 expression characterized tumors with aggressive behavior, whereas tumors with high TAp63 expression were significantly smaller and less aggressive. In salivary gland cells, high expression of ΔNp63 led to enhanced cell migration and invasion and suppression of cell senescence independent of TAp63 and/or TP53 gene status. We conclude the following: i) overexpression of ΔNp63 contributes to salivary tumorigenesis, ii) ΔNp63 plays a dominant negative effect on the TA isoform in the modulation of cell migration and invasion, and iii) the ΔN isoform plays an oncogenic role and may represent an attractive target for therapeutic intervention in patients with salivary carcinomas.
Copyright © 2011 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Pinkston J.A., Cole P. Incidence rates of salivary gland tumors: results from a population-based study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999;120:834–840. - PubMed
-
- Speight P.M., Barrett A.W. Salivary gland tumours. Oral Dis. 2002;8:229–240. - PubMed
-
- Terhaard C.H., Lubsen H., Van der Tweel I., Hilgers F.J., Eijkenboom W.M., Marres H.A., Tjho-Heslinga R.E., de Jong J.M., Roodenburg J.L., Dutch Head and Neck Oncology Cooperative Group Salivary gland carcinoma: independent prognostic factors for locoregional control, distant metastasis, and overall survival: results of the Dutch head and neck oncology cooperative group. Head Neck. 2004;26:681–692. discussion, 692–693. - PubMed
-
- Day T.A., Deveikis J., Gillespie M.B., Joe J.K., Ogretmen B., Osguthorpe J.D., Reed S.G., Richardson M.S., Rossi M., Saini R., Sharma A.K., Stuart R.K. Salivary gland neoplasms. Carr Treat Options Oncol. 2004;5:11–26. - PubMed
-
- Bron L.P., Traynor S.J., McNeil E.B., O'Brien C.J. Primary and metastatic cancer of the parotid: comparison of clinical behavior in 232 cases. Laryngoscope. 2003;113:1070–1075. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

