NLRX1 protein attenuates inflammatory responses to infection by interfering with the RIG-I-MAVS and TRAF6-NF-κB signaling pathways
- PMID: 21703540
- PMCID: PMC3166771
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.03.026
NLRX1 protein attenuates inflammatory responses to infection by interfering with the RIG-I-MAVS and TRAF6-NF-κB signaling pathways
Abstract
The nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich-repeat-containing (NLR) proteins regulate innate immunity. Although the positive regulatory impact of NLRs is clear, their inhibitory roles are not well defined. We showed that Nlrx1(-/-) mice exhibited increased expression of antiviral signaling molecules IFN-β, STAT2, OAS1, and IL-6 after influenza virus infection. Consistent with increased inflammation, Nlrx1(-/-) mice exhibited marked morbidity and histopathology. Infection of these mice with an influenza strain that carries a mutated NS-1 protein, which normally prevents IFN induction by interaction with RNA and the intracellular RNA sensor RIG-I, further exacerbated IL-6 and type I IFN signaling. NLRX1 also weakened cytokine responses to the 2009 H1N1 pandemic influenza virus in human cells. Mechanistically, Nlrx1 deletion led to constitutive interaction of MAVS and RIG-I. Additionally, an inhibitory function is identified for NLRX1 during LPS activation of macrophages where the MAVS-RIG-I pathway was not involved. NLRX1 interacts with TRAF6 and inhibits NF-κB activation. Thus, NLRX1 functions as a checkpoint of overzealous inflammation.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
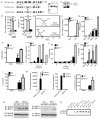
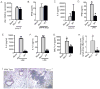

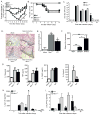

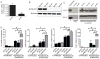
Comment in
-
NOD so fast: NLRX1 puts the brake on inflammation.Immunity. 2011 Jun 24;34(6):821-2. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.06.006. Immunity. 2011. PMID: 21703534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdul-Sater AA, Said-Sadier N, Lam VM, Singh B, Pettengill MA, Soares F, Tattoli I, Lipinski S, Girardin SE, Rosenstiel P, et al. Enhancement of reactive oxygenspecies production and chlamydial infection by the mitochondrial Nod like family member NLRX1. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:41637–41645. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benko S, Magalhaes JG, Philpott DJ, Girardin SE. NLRC5 limits the activation of inflammatory pathways. J Immunol. 2010;185:1681–1691. - PubMed
-
- Buchweitz JP, Harkema JR, Kaminski NE. Time-dependent airway epithelial and inflammatory cell responses induced by influenza virus A/PR/8/34 in C57BL/6 mice. Toxicol Pathol. 2007;35:424–435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA156330/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AI082895/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32-AI-082895-01/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009156/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI067798/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19-AI067798/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54-AI057157/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AI057157/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32-CA009156/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19-AI077437/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32-AR007416/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR007416/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI077437/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

