miR-21 and miR-214 are consistently modulated during renal injury in rodent models
- PMID: 21704009
- PMCID: PMC3157202
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.04.021
miR-21 and miR-214 are consistently modulated during renal injury in rodent models
Abstract
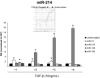
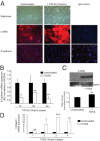
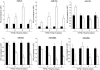
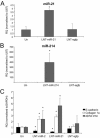
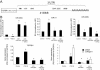
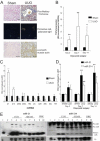
Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β is one of the main fibrogenic cytokines that drives the pathophysiology of progressive renal scarring. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous non-coding RNAs that post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression. We examined the role of TGF-β-induced expression of miR-21, miRNAs in cell culture models and miRNA expression in relevant models of renal disease. In vitro, TGF-β changed expression of miR-21, miR-214, and miR-145 in rat mesangial cells (CRL-2753) and miR-214, miR-21, miR-30c, miR-200b, and miR-200c during induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in rat tubular epithelial cells (NRK52E). miR-214 expression was robustly modulated in both cell types, whereas in tubular epithelial cells miR-21 was increased and miR-200b and miR-200c were decreased by 58% and 48%, respectively, in response to TGF-β. TGF-β receptor-1 was found to be a target of miR-200b/c and was down-regulated after overexpression of miR-200c. To assess the differential expression of these miRNAs in vivo, we used the anti-Thy1.1 mesangial glomerulonephritis model and the unilateral ureteral obstruction model in which TGF-β plays a role and also a genetic model of hypertension, the stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat with and without salt loading. The expressions of miR-214 and miR-21 were significantly increased in all in vivo models, showing a possible miRNA signature of renal damage despite differing causes.
Copyright © 2011 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
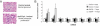

References
-
- Bottinger E.P., Bitzer M. TGF-{beta} signaling in renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:2600–2610. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y. Renal fibrosis: new insights into the pathogenesis and therapeutics. Kidney Int. 2006;69:213–217. - PubMed
-
- Schlondorff D. The glomerular mesangial cell: an expanding role for a specialized pericyte. FASEB J. 1987;1:272–281. - PubMed
-
- Whelton P.K., Klag M.J. Hypertension as a risk factor for renal disease: Review of clinical and epidemiological evidence. Hypertension. 1989;13:I19–I27. - PubMed
-
- Koh-Tan H.H., Graham D., Hamilton C.A., Nicoll G., Fields L., McBride M.W., Young B., Dominiczak A.F. Renal and vascular glutathione S-transferase mu is not affected by pharmacological intervention to reduce systolic blood pressure. J Hypertens. 2009;27:1575–1584. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

