Wnt2 signaling is necessary and sufficient to activate the airway smooth muscle program in the lung by regulating myocardin/Mrtf-B and Fgf10 expression
- PMID: 21704027
- PMCID: PMC3319016
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.06.011
Wnt2 signaling is necessary and sufficient to activate the airway smooth muscle program in the lung by regulating myocardin/Mrtf-B and Fgf10 expression
Abstract
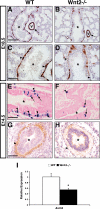
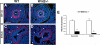
Smooth muscle in the lung is thought to derive from the developing lung mesenchyme. Smooth muscle formation relies upon coordination of both autocrine and paracrine signaling between the budding epithelium and adjacent mesenchyme to govern its proliferation and differentiation. However, the pathways initiating the earliest aspects of smooth muscle specification and differentiation in the lung are poorly understood. Here, we identify the Wnt2 ligand as a critical regulator of the earliest aspects of lung airway smooth muscle development. Using Wnt2 loss and gain of function models, we show that Wnt2 signaling is necessary and sufficient for activation of a transcriptional and signaling network critical for smooth muscle specification and differentiation including myocardin/Mrtf-B and the signaling factor Fgf10. These studies place Wnt2 high in a hierarchy of signaling molecules that promote the earliest aspects of lung airway smooth muscle development.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Bellusci S, Furuta Y, Rush MG, Henderson R, Winnier G, Hogan BL. Involvement of Sonic hedgehog (Shh) in mouse embryonic lung growth and morphogenesis. Development. 1997a;124:53–63. - PubMed
-
- Bellusci S, Grindley J, Emoto H, Itoh N, Hogan BL. Fibroblast growth factor 10 (FGF10) and branching morphogenesis in the embryonic mouse lung. Development. 1997b;124:4867–4878. - PubMed
-
- Betsholtz C. Insight into the physiological functions of PDGF through genetic studies in mice. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004;15:215–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

