Effect of purified Russell's viper venom-factor X activator (RVV-X) on renal hemodynamics, renal functions, and coagulopathy in rats
- PMID: 21704055
- PMCID: PMC3304456
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2011.05.007
Effect of purified Russell's viper venom-factor X activator (RVV-X) on renal hemodynamics, renal functions, and coagulopathy in rats
Abstract
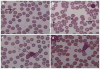
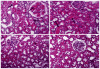
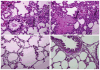
Acute renal failure (ARF) is the most frequent and a serious complication in victims of Russell's viper snakebites. Russell's viper venom-factor X activator (RVV-X) has been identified as a main procoagulant enzyme involving coagulopathy, which might be responsible for changes in renal hemodynamics and renal functions. Here, we purified RVV-X from crude Russell's viper venom to study renal hemodynamics, renal functions, intravascular clot, and histopathological changes in Sprague-Dawley rats. Changes in renal hemodynamics and renal functions were evaluated by measuring the mean arterial pressure, glomerular filtration rate (GFR), effective renal plasma flow (ERPF), effective renal blood flow (ERBF), renal vascular resistance (RVR), and fractional excretion of electrolytes. After 10 min, rats receiving both crude venom and purified RVV-X decreased GFR, ERPF, and ERBF and increased RVR. These changes correlated to renal lesions. Along with the determination of intravascular clot, rats injected with purified RVV-X increased the average D-dimer level and reached a peak at 10 min, declined temporarily, and then reached another peak at 30 min. The temporal association between clots and renal dysfunction was observed in rats within 10 min after the injection of purified RVV-X. These findings suggested RVV-X as a major cause of renal failure through intravascular clotting in the renal microcirculation.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Adam SS, Key NS, Greenberg CS. D-dimer antigen: current concepts and future prospects. Blood. 2009;113:2878–2887. - PubMed
-
- Adi-Bessalem S, Hammoudi-Triki D, Laraba-Djebari F. Pathophysiological effects of Androctonus australis hector scorpion venom: tissue damages and inflammatory response. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2008;60:373–380. - PubMed
-
- Bertazzi DT, de Assis-Pandochi AI, Talhaferro VL, Caleiro Seixas Azzolini AE, Pereira Crott LS, Arantes EC. Activation of the complement system and leukocyte recruitment by Tityus serrulatus scorpion venom. Int Immunopharmacol. 2005;5:1077–1084. - PubMed
-
- Burke TJ, Navar LG, Clapp JR, Robinson RR. Response to single nephron glomerular filtration rate to distal nephron microperfusion. Kidney Int. 1974;6:230–240. - PubMed
-
- Chan L, Chittinandana A, Shapiro JI, Shanley PF, Schrier RW. Effect of an endothelin-receptor antagonist on ischemic acute renal failure. Am J Physiol. 1994;266:F135–F138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

