High resolution of microRNA signatures in human whole saliva
- PMID: 21704302
- PMCID: PMC3189266
- DOI: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2011.05.015
High resolution of microRNA signatures in human whole saliva
Abstract
Objective: Identifying discriminatory human salivary RNA biomarkers reflective of disease in a low-cost non-invasive screening assay is crucial to salivary diagnostics. Recent studies have reported both mRNA and microRNA (miRNA) in saliva, but little information has been documented on the quality and yield of RNA collected. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to develop an improved RNA isolation method from saliva and to identify major miRNA species in human whole saliva.
Design: RNA samples were isolated from normal human saliva using a combined protocol based on the Oragene RNA collection kit and the mirVana miRNA isolation kit in tandem. RNA samples were analysed for quality and subjected to miRNA array analysis.
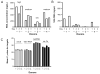
Results: RNA samples isolated from twenty healthy donors ranged from 2.59 to 29.4 μg/ml saliva and with 1.92-2.16OD(260/280 nm) ratios. RNA yield and concentration of saliva samples were observed to be stable over 48 h at room temperature. Analysis of total salivary RNA isolated from these twenty donors showed no statistical significance between sexes; however, the presence of high-, medium-, and low-yield salivary RNA producers was detected. MiRNA array analysis of salivary RNA detected five abundantly expressed miRNAs, miR-223, miR-191, miR-16, miR-203, and miR-24, that were similarly described in other published reports. Additionally, many previously undetected miRNAs were also identified.
Conclusion: High quality miRNAs can be isolated from saliva using available commercial kits, and in future studies, the availability of this isolation protocol may allow specific changes in their levels to be measured accurately in various relevant diseases.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Schipper RG, Silletti E, Vingerhoeds MH. Saliva as research material: biochemical, physicochemical and practical aspects. Arch Oral Biol. 2007;52:1114–35. - PubMed
-
- Dalmay T. MicroRNAs and cancer. J Intern Med. 2008;263:366–75. - PubMed
-
- Navazesh M. Methods for collecting saliva. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993;694:72–7. - PubMed
-
- Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Orntoft TF. Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res. 2004;64:5245–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

