Protein kinase signaling networks in plant innate immunity
- PMID: 21704551
- PMCID: PMC3191242
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbi.2011.05.006
Protein kinase signaling networks in plant innate immunity
Abstract
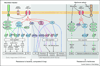
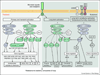
In plants and animals, innate immunity is triggered through pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) in response to microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) to provide the first line of inducible defense. Plant receptor protein kinases (RPKs) represent the main plasma membrane PRRs perceiving diverse MAMPs. RPKs also recognize secondary danger-inducible plant peptides and cell-wall signals. Both types of RPKs trigger rapid and convergent downstream signaling networks controlled by calcium-activated PKs and mitogen-activated PK (MAPK) cascades. These PK signaling networks serve specific and overlapping roles in controlling the activities and synthesis of a plethora of transcription factors (TFs), enzymes, hormones, peptides and antimicrobial chemicals, contributing to resistance against bacteria, oomycetes and fungi.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Dodds PN, Rathjen JP. Plant immunity: towards an integrated view of plant-pathogen interactions. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:539–548. - PubMed
-
-
Boller T, Felix G. A Renaissance of Elicitors: Perception of Microbe-Associated Molecular Patterns and Danger Signals by Pattern-Recognition Receptors. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2009;60:379–406. This is a comprehensive review on MAMPs and PRRs with a special emphasis on the time course of events following PRR activation. The model on defense syndrome nicely summaries plant perceptions of distinct microbial and plant damage-associated signals in evolutionary context and innate immunity.
-
-
- Ronald PC, Beutler B. Plant and Animal Sensors of Conserved Microbial Signatures. Science. 2010;330:1061–1064. - PubMed
-
-
Lacombe S, Rougon-Cardoso A, Sherwood E, Peeters N, Dahlbeck D, van Esse HP, Smoker M, Rallapalli G, Thomma BPHJ, Staskawicz B, et al. Interfamily transfer of a plant pattern-recognition receptor confers broad-spectrum bacterial resistance. Nat Biotech. 2010;28:365–369. This work provides the most compelling evidence that the activity of a PRR can be transferred among plant families and confers broad-spectrum bacterial resistance in important crops.
-
-
- He P, Shan L, Lin N-C, Martin GB, Kemmerling B, Nürnberger T, Sheen J. Specific Bacterial Suppressors of MAMP Signaling Upstream of MAPKKK in Arabidopsis Innate Immunity. Cell. 2006;125:563–575. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

