Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) incorporation into the brain from plasma, as an in vivo biomarker of brain DHA metabolism and neurotransmission
- PMID: 21704722
- PMCID: PMC3202024
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2011.06.003
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) incorporation into the brain from plasma, as an in vivo biomarker of brain DHA metabolism and neurotransmission
Abstract
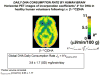
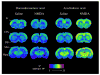
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is critical for maintaining normal brain structure and function, and is considered neuroprotective. Its brain concentration depends on dietary DHA content and hepatic conversion from its dietary derived n-3 precursor, α-linolenic acid (α-LNA). We have developed an in vivo method in rats using quantitative autoradiography and intravenously injected radiolabeled DHA to image net incorporation into the brain of unesterified plasma DHA, and showed with this method that the incorporation rate of DHA equals the rate of brain metabolic DHA consumption. The method has been extended for use in humans with positron emission tomography (PET). Furthermore, imaging in unanesthetized rats using DHA incorporation as a biomarker in response to acute N-methyl-D-aspartate administration confirms that regional DHA signaling is independent of extracellular calcium, and likely mediated by a calcium-independent phospholipase A(2) (iPLA(2)). Studies in mice in which iPLA(2)-VIA (β) was knocked out confirmed that this enzyme is critical for baseline and muscarinic cholinergic signaling involving DHA. Thus, quantitative imaging of DHA incorporation from plasma into brain can be used as an in vivo biomarker of brain DHA metabolism and neurotransmission.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
No author has a conflict of interest with regard to the research.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

