Effect of early intensive multifactorial therapy on 5-year cardiovascular outcomes in individuals with type 2 diabetes detected by screening (ADDITION-Europe): a cluster-randomised trial
- PMID: 21705063
- PMCID: PMC3136726
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60698-3
Effect of early intensive multifactorial therapy on 5-year cardiovascular outcomes in individuals with type 2 diabetes detected by screening (ADDITION-Europe): a cluster-randomised trial
Erratum in
- Lancet. 2012 Mar 3;379(9818):804
Abstract
Background: Intensive treatment of multiple cardiovascular risk factors can halve mortality among people with established type 2 diabetes. We investigated the effect of early multifactorial treatment after diagnosis by screening.
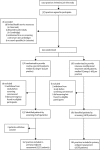
Methods: In a pragmatic, cluster-randomised, parallel-group trial done in Denmark, the Netherlands, and the UK, 343 general practices were randomly assigned screening of registered patients aged 40-69 years without known diabetes followed by routine care of diabetes or screening followed by intensive treatment of multiple risk factors. The primary endpoint was first cardiovascular event, including cardiovascular mortality and morbidity, revascularisation, and non-traumatic amputation within 5 years. Patients and staff assessing outcomes were unaware of the practice's study group assignment. Analysis was done by intention to treat. This study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT00237549.
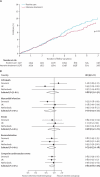
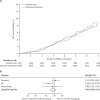
Findings: Primary endpoint data were available for 3055 (99·9%) of 3057 screen-detected patients. The mean age was 60·3 (SD 6·9) years and the mean duration of follow-up was 5·3 (SD 1·6) years. Improvements in cardiovascular risk factors (HbA(1c) and cholesterol concentrations and blood pressure) were slightly but significantly better in the intensive treatment group. The incidence of first cardiovascular event was 7·2% (13·5 per 1000 person-years) in the intensive treatment group and 8·5% (15·9 per 1000 person-years) in the routine care group (hazard ratio 0·83, 95% CI 0·65-1·05), and of all-cause mortality 6·2% (11·6 per 1000 person-years) and 6·7% (12·5 per 1000 person-years; 0·91, 0·69-1·21), respectively.
Interpretation: An intervention to promote early intensive management of patients with type 2 diabetes was associated with a small, non-significant reduction in the incidence of cardiovascular events and death.
Funding: National Health Service Denmark, Danish Council for Strategic Research, Danish Research Foundation for General Practice, Danish Centre for Evaluation and Health Technology Assessment, Danish National Board of Health, Danish Medical Research Council, Aarhus University Research Foundation, Wellcome Trust, UK Medical Research Council, UK NIHR Health Technology Assessment Programme, UK National Health Service R&D, UK National Institute for Health Research, Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care, University Medical Center, Utrecht, Novo Nordisk, Astra, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, Servier, HemoCue, Merck.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
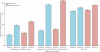
Comment in
-
The case for diabetes screening: ADDITION-Europe.Lancet. 2011 Jul 9;378(9786):106-8. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60819-2. Epub 2011 Jun 24. Lancet. 2011. PMID: 21705070 No abstract available.
-
ADDITION-Europe and the case for diabetes screening.Lancet. 2012 Jan 28;379(9813):313; author reply 313-4. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60142-1. Lancet. 2012. PMID: 22284655 No abstract available.
References
-
- IDF . IDF Diabetes Atlas. 4th edn. International Diabetes Federation; Brussels, Belgium: 2009.
-
- Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, Jensen GV, Parving HH, Pedersen O. Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:383–393. - PubMed
-
- Gaede P, Lund-Andersen H, Parving HH, Pedersen O. Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:580–591. - PubMed
-
- Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study Investigators Effects of ramipril on cardiovascular and microvascular outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus: results of the HOPE study and MICRO-HOPE substudy. Lancet. 2000;355:253–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

