CsrA and TnaB coregulate tryptophanase activity to promote exotoxin-induced killing of Caenorhabditis elegans by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli
- PMID: 21705596
- PMCID: PMC3165518
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.05197-11
CsrA and TnaB coregulate tryptophanase activity to promote exotoxin-induced killing of Caenorhabditis elegans by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli
Abstract
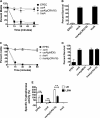
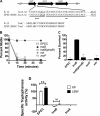
Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli(EPEC) requires the tnaA-encoded enzyme tryptophanase and its substrate tryptophan to synthesize diffusible exotoxins that kill the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Here, we demonstrate that the RNA-binding protein CsrA and the tryptophan permease TnaB coregulate tryptophanase activity, through mutually exclusive pathways, to stimulate toxin-mediated paralysis and killing of C. elegans.
Figures

References
-
- Aballay A., Ausubel F. M. 2002. Caenorhabditis elegansas a host for the study of host-pathogen interactions. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 5:97–101 - PubMed
-
- Anyanful A., et al. 2005. Paralysis and killing of Caenorhabditis elegansby enteropathogenic Escherichia colirequires the bacterial tryptophanase gene. Mol. Microbiol. 57:988–1007 - PubMed
-
- Baker C. S., Morozov I., Suzuki K., Romeo T., Babitzke P. 2002. CsrA regulates glycogen biosynthesis by preventing translation of glgCin Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 44:1599–1610 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

