PKCα mediates acetylcholine-induced activation of TRPV4-dependent calcium influx in endothelial cells
- PMID: 21705673
- PMCID: PMC3302191
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00142.2011
PKCα mediates acetylcholine-induced activation of TRPV4-dependent calcium influx in endothelial cells
Abstract
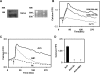
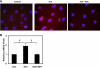
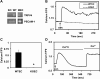
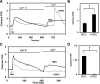
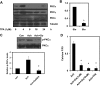
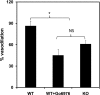
Transient receptor potential vanilloid channel 4 (TRPV4) is a polymodally activated nonselective cationic channel implicated in the regulation of vasodilation and hypertension. We and others have recently shown that cyclic stretch and shear stress activate TRPV4-mediated calcium influx in endothelial cells (EC). In addition to the mechanical forces, acetylcholine (ACh) was shown to activate TRPV4-mediated calcium influx in endothelial cells, which is important for nitric oxide-dependent vasodilation. However, the molecular mechanism through which ACh activates TRPV4 is not known. Here, we show that ACh-induced calcium influx and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) phosphorylation but not calcium release from intracellular stores is inhibited by a specific TRPV4 antagonist, AB-159908. Importantly, activation of store-operated calcium influx was not altered in the TRPV4 null EC, suggesting that TRPV4-dependent calcium influx is mediated through a receptor-operated pathway. Furthermore, we found that ACh treatment activated protein kinase C (PKC) α, and inhibition of PKCα activity by the specific inhibitor Go-6976, or expression of a kinase-dead mutant of PKCα but not PKCε or downregulation of PKCα expression by chronic 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate treatment, completely abolished ACh-induced calcium influx. Finally, we found that ACh-induced vasodilation was inhibited by the PKCα inhibitor Go-6976 in small mesenteric arteries from wild-type mice, but not in TRPV4 null mice. Taken together, these findings demonstrate, for the first time, that a specific isoform of PKC, PKCα, mediates agonist-induced receptor-mediated TRPV4 activation in endothelial cells.
Figures


References
-
- Becker D, Muller M, Leuner K, Jendrach M. The C-terminal domain of TRPV4 is essential for plasma membrane localization. Mol Membr Biol 25: 139–151, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Cesare P, Dekker LV, Sardini A, Parker PJ, McNaughton PA. Specific involvement of PKC-epsilon in sensitization of the neuronal response to painful heat. Neuron 23: 617–624, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Drexler H, Hornig B. Endothelial dysfunction in human disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol 31: 51–60, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

