Generation and detection of levuglandins and isolevuglandins in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 21705973
- PMCID: PMC6264246
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules16075333
Generation and detection of levuglandins and isolevuglandins in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
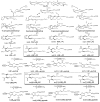
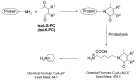
Levuglandins (LGs) and isolevuglandins (isoLGs), formed by rearrangement of endoperoxide intermediates generated through the cyclooxygenase and free radical induced oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), are extraordinarily reactive, forming covalent adducts incorporating protein lysyl ε-amino groups. Because they accumulate, these adducts provide a dosimeter of oxidative injury. This review provides an updated and comprehensive overview of the generation of LG/isoLG in vitro and in vivo and the detection methods for the adducts of LG/isoLG and biological molecules in vivo.
Figures


References
-
- Davies S.S., Amarnath V., Montine K.S., Bernoud-Hubac N., Boutaud O., Montine T.J., Roberts L.J., 2nd Effects of reactive gamma-ketoaldehydes formed by the isoprostane pathway (isoketals) and cyclooxygenase pathway (levuglandins) on proteasome function. FASEB J. 2002;16:715–717. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0696fje. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

