NF-κB mediates radio-sensitization by the PARP-1 inhibitor, AG-014699
- PMID: 21706052
- PMCID: PMC3191117
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2011.229
NF-κB mediates radio-sensitization by the PARP-1 inhibitor, AG-014699
Erratum in
-
Correction to: NF-κB mediates radio-sensitization by the PARP-1 inhibitor, AG-014699.Oncogene. 2023 Feb;42(6):471. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02524-2. Oncogene. 2023. PMID: 36482204 No abstract available.
Abstract
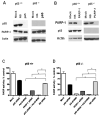
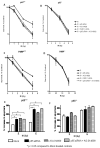
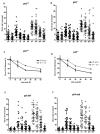
The stress-inducible transcription factor, nuclear factor (NF)-κB induces genes involved in proliferation and apoptosis. Aberrant NF-κB activity is common in cancer and contributes to therapeutic-resistance. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) is activated during DNA strand break repair and is a known transcriptional co-regulator. Here, we investigated the role of PARP-1 function during NF-κB activation using p65 small interfering RNA (siRNA), PARP siRNA or the potent PARP-1 inhibitor, AG-014699. Survival and apoptosis assays showed that NF-κB p65(-/-) cells were more sensitive to ionizing radiation (IR) than p65(+/+) cells. Co-incubation with p65 siRNA, PARP siRNA or AG-014699 radio-sensitized p65(+/+), but not p65(-/-) cells, demonstrating that PARP-1 mediates its effects on survival via NF-κB. Single-strand break (SSB) repair kinetics, and the effect SSB repair inhibition by AG-014699 were similar in p65(+/+) and p65(-/-) cells. As preventing SSB repair did not radio-sensitize p65(-/-) cells, we conclude that radio-sensitization by AG-014699 is due to downstream inhibition of NF-κB activation, and independent of SSB repair inhibition. PARP-1 catalytic activity was essential for IR-induced p65 DNA binding and NF-κB-dependent gene transcription, whereas for tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-treated cells, PARP-1 protein alone was sufficient. We hypothesize that this stimulus-dependent differential is mediated via stimulation of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymer, which was induced following IR, not TNF-α. Targeting DNA damage-activated NF-κB using AG-014699 may therefore overcome toxicity observed with classical NF-κB inhibitors without compromising other vital inflammatory functions. These data highlight the potential of PARP-1 inhibitors to overcome NF-κB-mediated therapeutic resistance and widens the spectrum of cancers in which these agents may be utilized.
Figures



References
-
- Althaus FR, Hofferer L, Kleczkowska HE, Malanga M, Naegeli H, Panzeter PL, et al. Histone shuttling by poly ADP-ribosylation. Mol Cell Biochem. 1994;138:53–9. - PubMed
-
- Barkett M, Gilmore T. Control of apoptosis by Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene. 1999;18:6910–24. - PubMed
-
- Basseres DS, Baldwin AS. Nuclear factor-kappaB and inhibitor of kappaB kinase pathways in oncogenic initiation and progression. Oncogene. 2006;25:6817–6830. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

