Small molecule inhibitors of ezrin inhibit the invasive phenotype of osteosarcoma cells
- PMID: 21706056
- PMCID: PMC3513970
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2011.245
Small molecule inhibitors of ezrin inhibit the invasive phenotype of osteosarcoma cells
Abstract
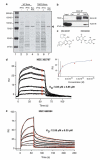
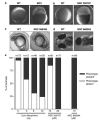
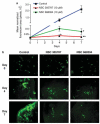
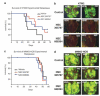
Ezrin is a multifunctional protein that connects the actin cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix through transmembrane proteins. High ezrin expression is associated with lung metastasis and poor survival in cancer. We screened small molecule libraries for compounds that directly interact with ezrin protein using surface plasmon resonance to identify lead compounds. The secondary functional assays used for lead compound selection included ezrin phosphorylation as measured by immunoprecipitation and in vitro kinase assays, actin binding, chemotaxis, invasion into an endothelial cell monolayer, zebrafish and Xenopus embryonic development, mouse lung organ culture and an in vivo lung metastasis model. Two molecules, NSC305787 and NSC668394, that directly bind to ezrin with low micromolar affinity were selected based on inhibition of ezrin function in multiple assays. They inhibited ezrin phosphorylation, ezrin-actin interaction and ezrin-mediated motility of osteosarcoma (OS) cells in culture. NSC305787 mimicked the ezrin morpholino phenotype, and NSC668394 caused a unique developmental defect consistent with reduced cell motility in zebrafish. Following tail vein injection of OS cells into mice, both molecules inhibited lung metastasis of ezrin-sensitive cells, but not ezrin-resistant cells. The small molecule inhibitors NSC305787 and NSC668394 demonstrate a novel targeted therapy that directly inhibits ezrin protein as an approach to prevent tumor metastasis.
Figures


References
-
- Bacci G, Longhi A, Cesari M, Versari M, Bertoni F. Influence of local recurrence on survival in patients with extremity osteosarcoma treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy: the experience of a single institution with 44 patients. Cancer. 2006;106:2701–2706. - PubMed
-
- Bayly C, Cieplak P, Cornell WD, Kollman PA. A well-behaved electrostatic potential based method using charge restraints for deriving atomic charges: the RESP model. J Phys Chem. 1993;97:10269–10280.
-
- Boger DL, Yasuda M, Mitscher LA, Drake SD, Kitos PA, Thompson SC. Streptonigrin and lavendamycin partial structures. Probes for the minimum, potent pharmacophore of streptonigrin, lavendamycin, and synthetic quinoline-5,8-diones. J Med Chem. 1987;30:1918–1928. - PubMed
-
- Bretscher A, Edwards K, Fehon RG. ERM proteins and merlin: integrators at the cell cortex. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:586–599. - PubMed
-
- Case DA, Darden TA, Cheatham TE, III, Simmerling CL, Wang J, Duke RE, et al. AMBER 8. University of California at San Francisco; San Francisco: 2004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

