Activation of MAPK/c-Fos induced responses in oral epithelial cells is specific to Candida albicans and Candida dubliniensis hyphae
- PMID: 21706283
- PMCID: PMC3257392
- DOI: 10.1007/s00430-011-0209-y
Activation of MAPK/c-Fos induced responses in oral epithelial cells is specific to Candida albicans and Candida dubliniensis hyphae
Abstract
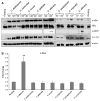
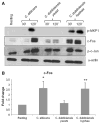
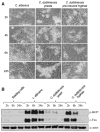
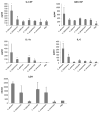
Oral epithelial cells detect the human pathogenic fungus Candida albicans via NF-κB and a bi-phasic mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling response. However, discrimination between C. albicans yeast and hyphal forms is mediated only by the MAPK pathway, which constitutes activation of the MAPK phosphatase MKP1 and the c-Fos transcription factor and is targeted against the hyphal form. Given that C. albicans is not the only Candida species capable of filamentation or causing mucosal infections, we sought to determine whether this MAPK/MKP1/c-Fos mediated response mechanism was activated by other pathogenic Candida species, including C. dubliniensis, C. tropicalis, C. parapsilosis, C. glabrata and C. krusei. Although all Candida species activated the NF-κB signaling pathway, only C. albicans and C. dubliniensis were capable of inducing MKP1 and c-Fos activation, which directly correlated with hypha formation. However, only C. albicans strongly induced cytokine production (G-CSF, GM-CSF, IL-6 and IL-1α) and cell damage. Candida dubliniensis, C. tropicalis and C. parapsilosis were also capable of inducing IL-1α and this correlated with mild cell damage and was dependent upon fungal burdens. Our data demonstrate that activation of the MAPK/MKP1/c-Fos pathway in oral epithelial cells is specific to C. dubliniensis and C. albicans hyphae.
Figures

References
-
- Odds FC. Candida and Candidosis. Bailliere Tindall; Philadelphia: 1988.
-
- Jayatilake J, Samaranayake Y, Samaranayake L. A comparative study of candidal invasion in rabbit tongue mucosal explants and reconstituted human oral epithelium. Mycopathologia. 2008;165:373–380. - PubMed
-
- Jayatilake JAMS, Samaranayake YH, Cheung LK, Samaranayake LP. Quantitative evaluation of tissue invasion by wild type, hyphal and SAP mutants of Candida albicans, and non-albicans Candida species in reconstituted human oral epithelium. J Oral Pathol Med. 2006;35:484–491. - PubMed
-
- Schaller M, Mailhammer R, Grassl G, Sander CA, Hube B, Korting HC. Infection of human oral epithelia with Candida species induces cytokine expression correlated to the degree of virulence. J Invest Dermatol. 2002;118:652–657. - PubMed
-
- Jayatilake JA, Samaranayake LP, Lu Q, Jin LJ. IL-1alpha, IL-1ra and IL-8 are differentially induced by Candida in experimental oral candidiasis. Oral Dis. 2007;13:426–433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

