Biweekly rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, non-pegylated liposome-encapsulated doxorubicin and prednisone (R-COMP-14) in elderly patients with poor-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and moderate to high 'life threat' impact cardiopathy
- PMID: 21707585
- PMCID: PMC3258483
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2011.08786.x
Biweekly rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, non-pegylated liposome-encapsulated doxorubicin and prednisone (R-COMP-14) in elderly patients with poor-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and moderate to high 'life threat' impact cardiopathy
Abstract
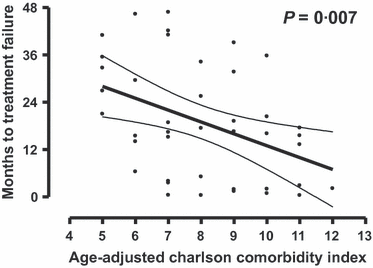
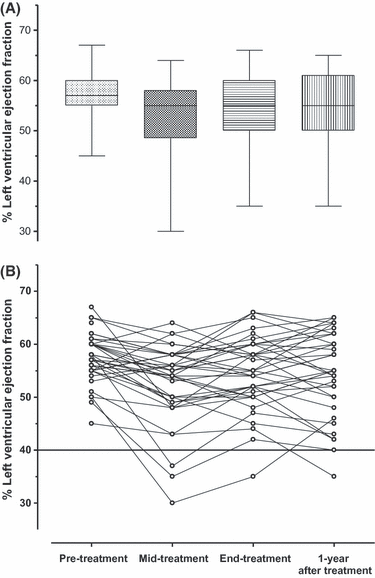
This Phase II study assessed feasibility and efficacy of a biweekly R-COMP-14 regimen (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, non-pegylated liposome-encapsulated doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone) in untreated elderly patients with poor-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and moderate to high 'life threat' impact NIA/NCI cardiac comorbidity. A total of 208 courses were delivered, with close cardiac monitoring, to 41 patients (median age: 73years, range: 62-82; 37% >75years) at a median interval of 15·6 (range, 13-29) days; 67% completed all six scheduled courses. Response rate was 73%, with 68% complete responses (CR); 4-year disease-free survival (DFS) and time to treatment failure (TTF) were 72% and 49%, respectively. Failures were due to early death (n=3), therapy discontinuations (no-response n=2; toxicity n=6), relapse (n=6) and death in CR (n=3). Incidence of cardiac grade 3-5 adverse events was 7/41 (17%; 95% confidence interval: 8-31%). Time to progression and overall survival at 4-years were 77% and 67%, respectively. The Age-adjusted Charlson Comorbidity Index (aaCCI) correlated with failures (P=0·007) with patients scoring ≤7 having a longer TTF (66% vs. 29%; P=0·009). R-COMP-14 is feasible and ensures a substantial DFS to poor-risk DLBCL patients who would have been denied anthracycline-based treatment due to cardiac morbidity. The aaCCI predicted both treatment discontinuation rate and TTF.
© 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Aapro M, Bernard-Marty C, Brain EG, Batist G, Erdkamp F, Krzemieniecki K, Leonard R, Lluch A, Monfardini S, Ryberg M, Soubeyran P, Wedding U. Anthracycline cardiotoxicity in the elderly cancer patient: a SIOG expert position paper. Annals of Oncology. 2010;22:257–267. - PubMed
-
- Allen TM, Martin FJ. Advantages of liposomal delivery systems for anthracyclines. Seminars in Oncology. 2004;31:5–15. - PubMed
-
- Altena R, Perik PJ, van Veldhuisen DJ, de Vries EG, Gietema JA. Cardiovascular toxicity caused by cancer treatment: strategies for early detection. The Lancet Oncology. 2009;10:391–399. - PubMed
-
- Ammann P, Fehr T, Minder EI, Gunter C, Bertel O. Elevation of troponin I in sepsis and septic shock. Intensive Care Medicine. 2001;27:965–969. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

